Domain Adaption Paper Reading List
[dranet dann dfa-mcd kd3a dsn deep-learning proda shot spl srda meda pcida fixbi contrastive-adaptation-network mean-teacher ta3n ran domain-adaption This is the my reading list of papers on domain adaption. This list is based on paperswithcode
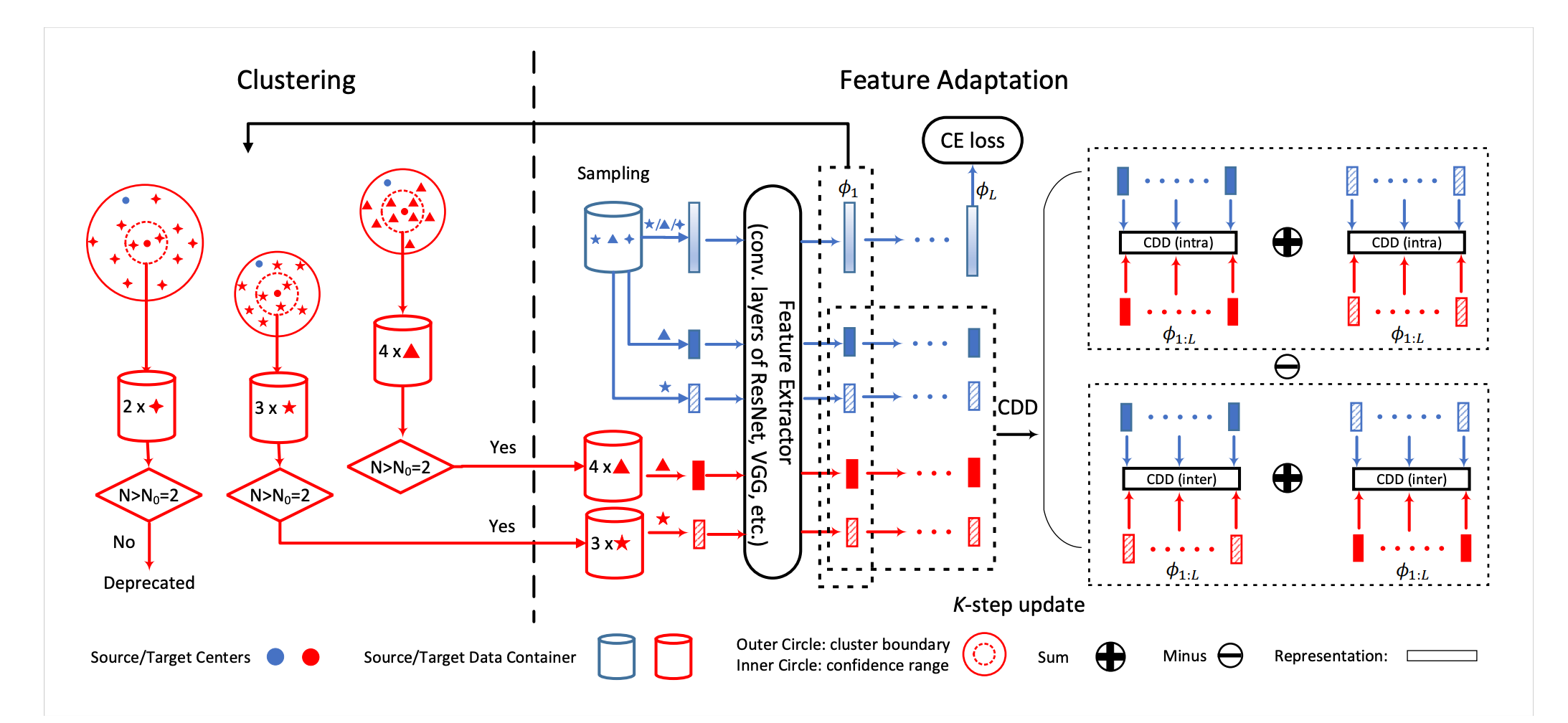
Contrastive Adaptation Network for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
CVPR 2019
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) makes predictions for the target domain data while manual annotations are only available in the source domain. Previous methods minimize the domain discrepancy neglecting the class information, which may lead to misalignment and poor generalization performance. To address this issue, this paper proposes Contrastive Adaptation Network (CAN) optimizing a new metric which explicitly models the intra-class domain discrepancy and the inter-class domain discrepancy. We design an alternating update strategy for training CAN in an end-to-end manner. Experiments on two real-world benchmarks Office-31 and VisDA-2017 demonstrate that CAN performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods and produces more discriminative features.
Prototypical Pseudo Label Denoising and Target Structure Learning for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Self-training is a competitive approach in domain adaptive segmentation, which trains the network with the pseudo labels on the target domain. However inevitably, the pseudo labels are noisy and the target features are dispersed due to the discrepancy between source and target domains. In this paper, we rely on representative prototypes, the feature centroids of classes, to address the two issues for unsupervised domain adaptation. In particular, we take one step further and exploit the feature distances from prototypes that provide richer information than mere prototypes. Specifically, we use it to estimate the likelihood of pseudo labels to facilitate online correction in the course of training. Meanwhile, we align the prototypical assignments based on relative feature distances for two different views of the same target, producing a more compact target feature space. Moreover, we find that distilling the already learned knowledge to a self-supervised pretrained model further boosts the performance. Our method shows tremendous performance advantage over state-of-the-art methods. We will make the code publicly available.
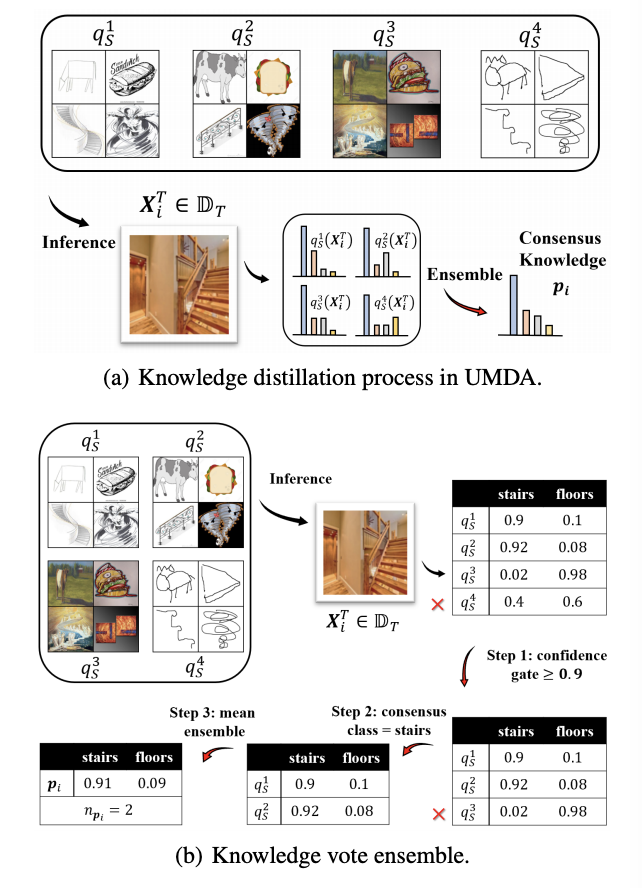
KD3A: Unsupervised Multi-Source Decentralized Domain Adaptation via Knowledge Distillation
ICML 2021
Conventional unsupervised multi-source domain adaptation (UMDA) methods assume all source domains can be accessed directly. This neglects the privacy-preserving policy, that is, all the data and computations must be kept decentralized. There exists three problems in this scenario: (1) Minimizing the domain distance requires the pairwise calculation of the data from source and target domains, which is not accessible. (2) The communication cost and privacy security limit the application of UMDA methods (e.g., the domain adversarial training). (3) Since users have no authority to check the data quality, the irrelevant or malicious source domains are more likely to appear, which causes negative transfer. In this study, we propose a privacy-preserving UMDA paradigm named Knowledge Distillation based Decentralized Domain Adaptation (KD3A), which performs domain adaptation through the knowledge distillation on models from different source domains. KD3A solves the above problems with three components: (1) A multi-source knowledge distillation method named Knowledge Vote to learn high-quality domain consensus knowledge. (2) A dynamic weighting strategy named Consensus Focus to identify both the malicious and irrelevant domains. (3) A decentralized optimization strategy for domain distance named BatchNorm MMD. The extensive experiments on DomainNet demonstrate that KD3A is robust to the negative transfer and brings a 100x reduction of communication cost compared with other decentralized UMDA methods. Moreover, our KD3A significantly outperforms state-of-the-art UMDA approaches.
Domain Separation Networks
NIPS 2016
The cost of large scale data collection and annotation often makes the application of machine learning algorithms to new tasks or datasets prohibitively expensive. One approach circumventing this cost is training models on synthetic data where annotations are provided automatically. Despite their appeal, such models often fail to generalize from synthetic to real images, necessitating domain adaptation algorithms to manipulate these models before they can be successfully applied. Existing approaches focus either on mapping representations from one domain to the other, or on learning to extract features that are invariant to the domain from which they were extracted. However, by focusing only on creating a mapping or shared representation between the two domains, they ignore the individual characteristics of each domain. We suggest that explicitly modeling what is unique to each domain can improve a model’s ability to extract domain-invariant features. Inspired by work on private-shared component analysis, we explicitly learn to extract image representations that are partitioned into two subspaces: one component which is private to each domain and one which is shared across domains. Our model is trained not only to perform the task we care about in the source domain, but also to use the partitioned representation to reconstruct the images from both domains. Our novel architecture results in a model that outperforms the state-of-the-art on a range of unsupervised domain adaptation scenarios and additionally produces visualizations of the private and shared representations enabling interpretation of the domain adaptation process.
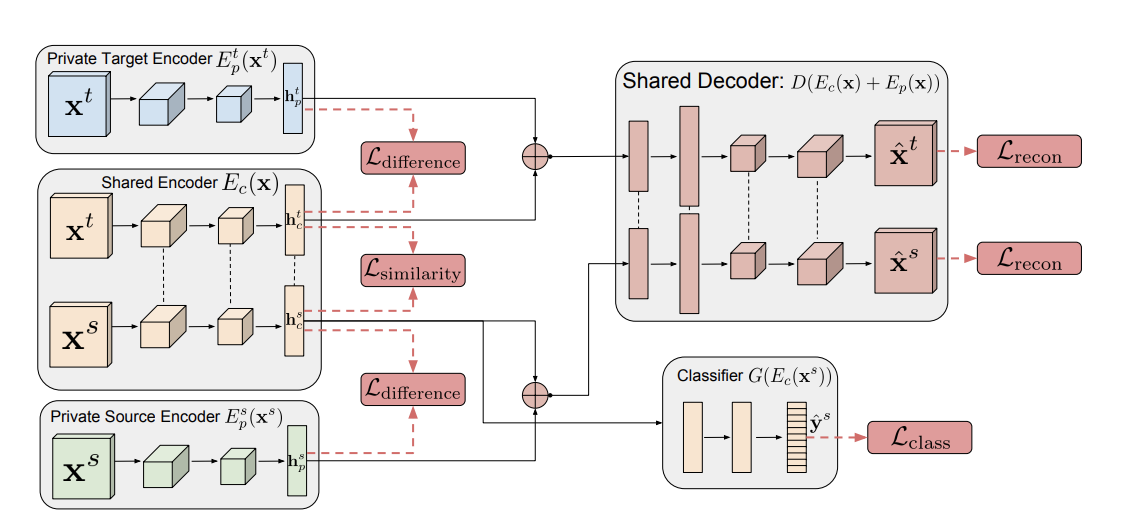
Visual Domain Adaptation with Manifold Embedded Distribution Alignment
Visual domain adaptation aims to learn robust classifiers for the target domain by leveraging knowledge from a source domain. Existing methods either attempt to align the cross-domain distributions, or perform manifold subspace learning. However, there are two significant challenges: (1) degenerated feature transformation, which means that distribution alignment is often performed in the original feature space, where feature distortions are hard to overcome. On the other hand, subspace learning is not sufficient to reduce the distribution divergence. (2) unevaluated distribution alignment, which means that existing distribution alignment methods only align the marginal and conditional distributions with equal importance, while they fail to evaluate the different importance of these two distributions in real applications. In this paper, we propose a Manifold Embedded Distribution Alignment (MEDA) approach to address these challenges. MEDA learns a domain-invariant classifier in Grassmann manifold with structural risk minimization, while performing dynamic distribution alignment to quantitatively account for the relative importance of marginal and conditional distributions. To the best of our knowledge, MEDA is the first attempt to perform dynamic distribution alignment for manifold domain adaptation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MEDA shows significant improvements in classification accuracy compared to state-of-the-art traditional and deep methods.
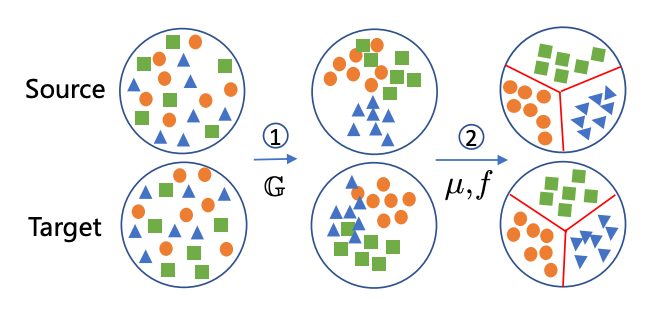
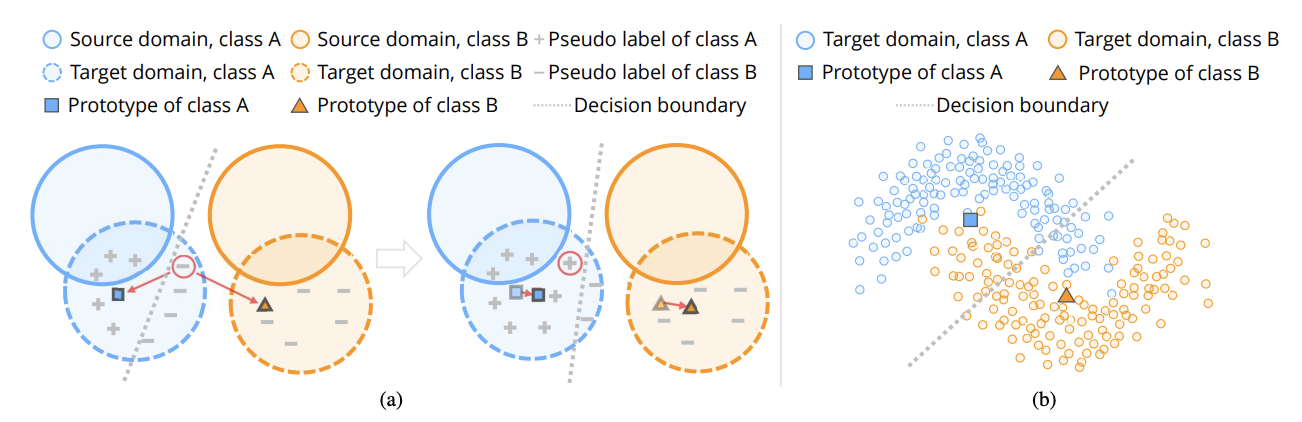
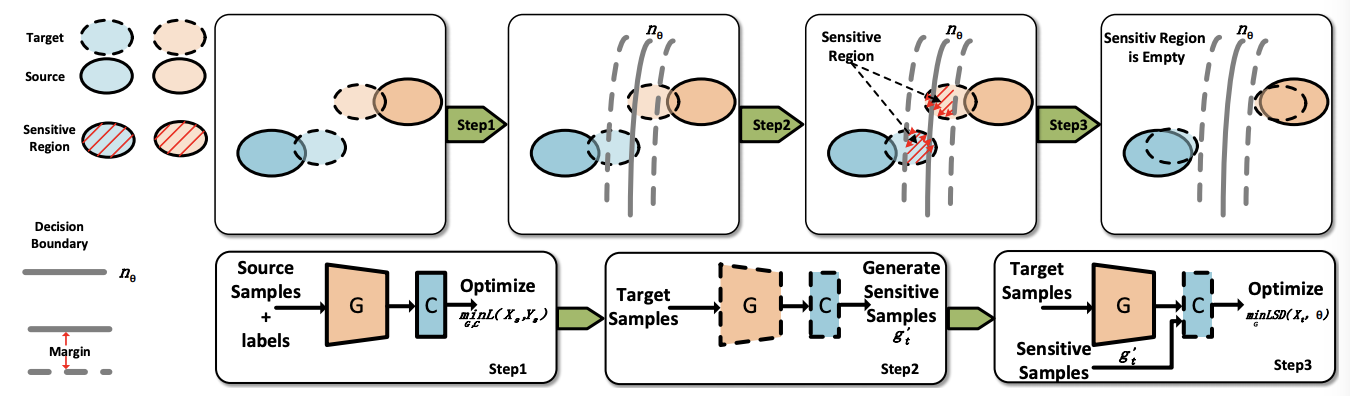
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation via Structured Prediction Based Selective Pseudo-Labeling
Unsupervised domain adaptation aims to address the problem of classifying unlabeled samples from the target domain whilst labeled samples are only available from the source domain and the data distributions are different in these two domains. As a result, classifiers trained from labeled samples in the source domain suffer from significant performance drop when directly applied to the samples from the target domain. To address this issue, different approaches have been proposed to learn domain-invariant features or domain-specific classifiers. In either case, the lack of labeled samples in the target domain can be an issue which is usually overcome by pseudo-labeling. Inaccurate pseudo-labeling, however, could result in catastrophic error accumulation during learning. In this paper, we propose a novel selective pseudo-labeling strategy based on structured prediction. The idea of structured prediction is inspired by the fact that samples in the target domain are well clustered within the deep feature space so that unsupervised clustering analysis can be used to facilitate accurate pseudo-labeling. Experimental results on four datasets (i.e. Office-Caltech, Office31, ImageCLEF-DA and Office-Home) validate our approach outperforms contemporary state-of-the-art methods.
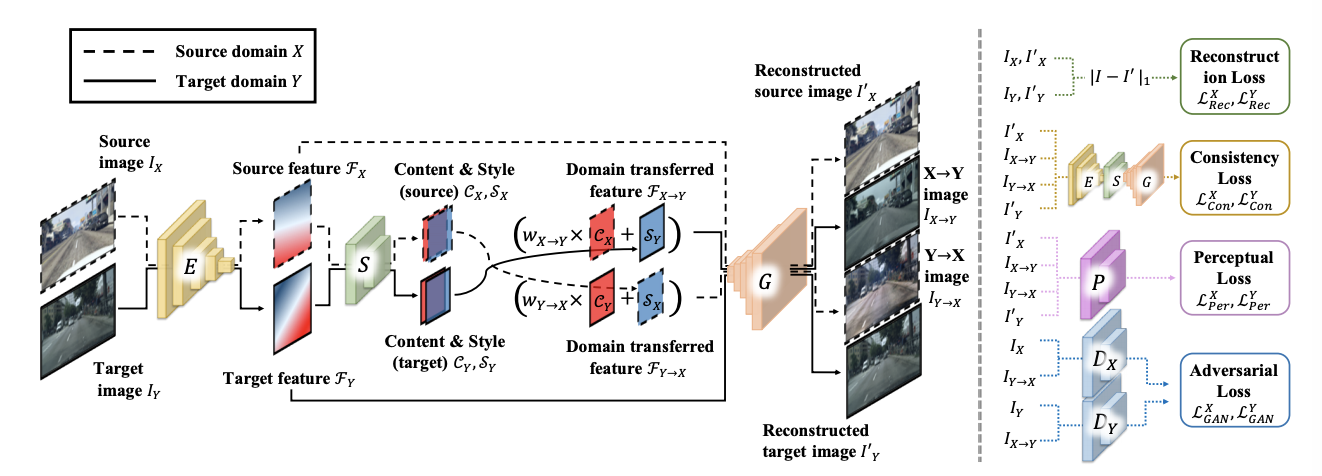
DRANet: Disentangling Representation and Adaptation Networks for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Adaptation
In this paper, we present DRANet, a network architecture that disentangles image representations and transfers the visual attributes in a latent space for unsupervised cross-domain adaptation. Unlike the existing domain adaptation methods that learn associated features sharing a domain, DRANet preserves the distinctiveness of each domain’s characteristics. Our model encodes individual representations of content (scene structure) and style (artistic appearance) from both source and target images. Then, it adapts the domain by incorporating the transferred style factor into the content factor along with learnable weights specified for each domain. This learning framework allows bi-/multi-directional domain adaptation with a single encoder-decoder network and aligns their domain shift. Additionally, we propose a content-adaptive domain transfer module that helps retain scene structure while transferring style. Extensive experiments show our model successfully separates content-style factors and synthesizes visually pleasing domain-transferred images. The proposed method demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on standard digit classification tasks as well as semantic segmentation tasks.
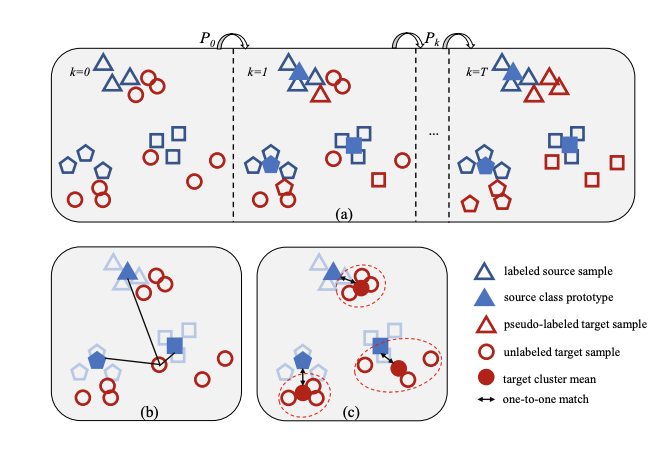
Learning Smooth Representation for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
In unsupervised domain adaptation, existing methods have achieved remarkable performance, but few pay attention to the Lipschitz constraint. It has been studied that not just reducing the divergence between distributions, but the satisfaction of Lipschitz continuity guarantees an error bound for the target distribution. In this paper, we adopt this principle and extend it to a deep end-to-end model. We define a formula named local smooth discrepancy to measure the Lipschitzness for target distribution in a pointwise way. Further, several critical factors affecting the error bound are taken into account in our proposed optimization strategy to ensure the effectiveness and stability. Empirical evidence shows that the proposed method is comparable or superior to the state-of-the-art methods and our modifications are important for the validity.
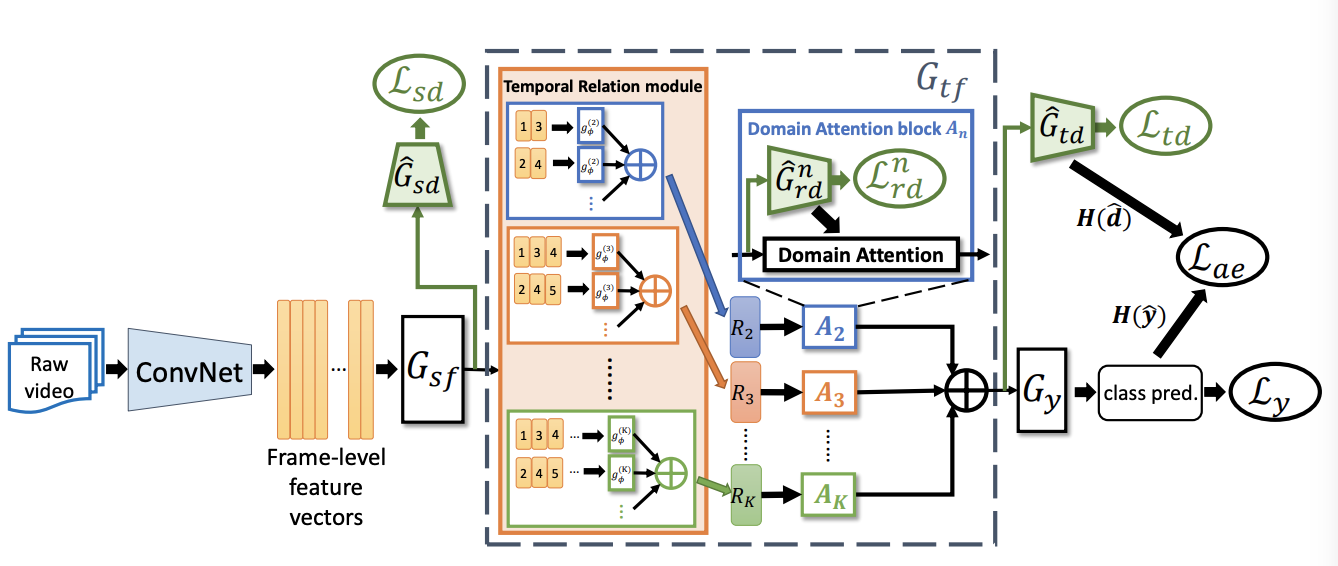
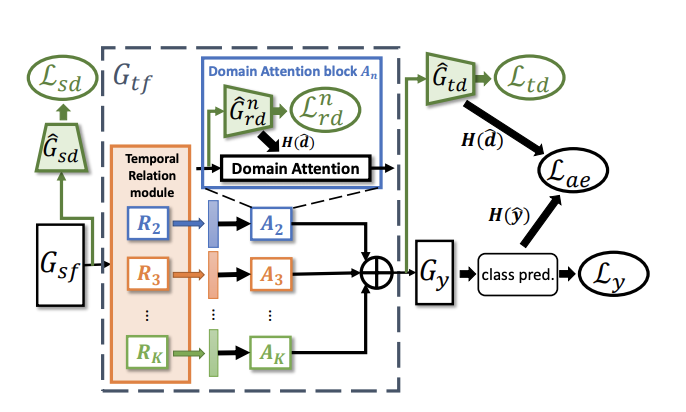
Temporal Attentive Alignment for Large-Scale Video Domain Adaptation
ICCV 2019
Although various image-based domain adaptation (DA) techniques have been proposed in recent years, domain shift in videos is still not well-explored. Most previous works only evaluate performance on small-scale datasets which are saturated. Therefore, we first propose two large-scale video DA datasets with much larger domain discrepancy: UCF-HMDB_full and Kinetics-Gameplay. Second, we investigate different DA integration methods for videos, and show that simultaneously aligning and learning temporal dynamics achieves effective alignment even without sophisticated DA methods. Finally, we propose Temporal Attentive Adversarial Adaptation Network (TA3N), which explicitly attends to the temporal dynamics using domain discrepancy for more effective domain alignment, achieving state-of-the-art performance on four video DA datasets (e.g. 7.9% accuracy gain over “Source only” from 73.9% to 81.8% on “HMDB –> UCF”, and 10.3% gain on “Kinetics –> Gameplay”). The code and data are released at http://github.com/cmhungsteve/TA3N.
Temporal Attentive Alignment for Video Domain Adaptation
Although various image-based domain adaptation (DA) techniques have been proposed in recent years, domain shift in videos is still not well-explored. Most previous works only evaluate performance on small-scale datasets which are saturated. Therefore, we first propose a larger-scale dataset with larger domain discrepancy: UCF-HMDB_full. Second, we investigate different DA integration methods for videos, and show that simultaneously aligning and learning temporal dynamics achieves effective alignment even without sophisticated DA methods. Finally, we propose Temporal Attentive Adversarial Adaptation Network (TA3N), which explicitly attends to the temporal dynamics using domain discrepancy for more effective domain alignment, achieving state-of-the-art performance on three video DA datasets. The code and data are released at http://github.com/cmhungsteve/TA3N
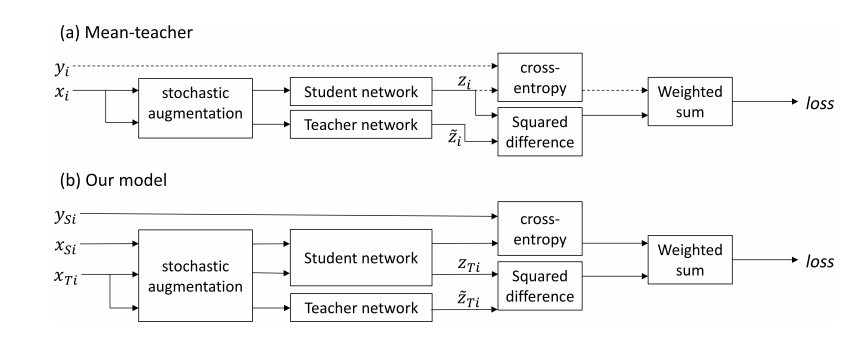
Self-ensembling for visual domain adaptation
ICLR 2018
This paper explores the use of self-ensembling for visual domain adaptation problems. Our technique is derived from the mean teacher variant (Tarvainen et al., 2017) of temporal ensembling (Laine et al;, 2017), a technique that achieved state of the art results in the area of semi-supervised learning. We introduce a number of modifications to their approach for challenging domain adaptation scenarios and evaluate its effectiveness. Our approach achieves state of the art results in a variety of benchmarks, including our winning entry in the VISDA-2017 visual domain adaptation challenge. In small image benchmarks, our algorithm not only outperforms prior art, but can also achieve accuracy that is close to that of a classifier trained in a supervised fashion.
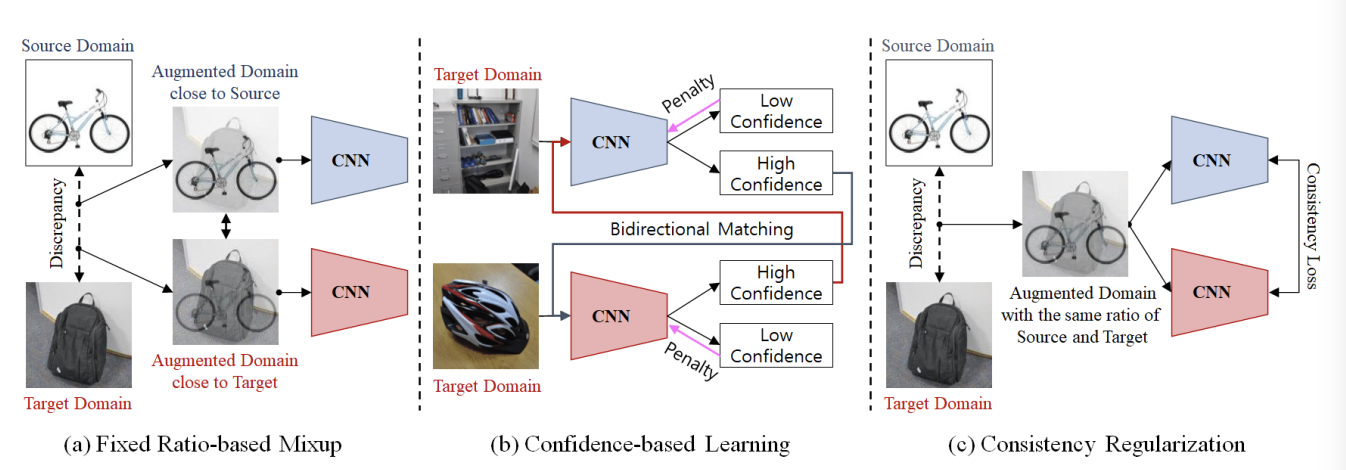
FixBi: Bridging Domain Spaces for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) methods for learning domain invariant representations have achieved remarkable progress. However, most of the studies were based on direct adaptation from the source domain to the target domain and have suffered from large domain discrepancies. In this paper, we propose a UDA method that effectively handles such large domain discrepancies. We introduce a fixed ratio-based mixup to augment multiple intermediate domains between the source and target domain. From the augmented-domains, we train the source-dominant model and the target-dominant model that have complementary characteristics. Using our confidence-based learning methodologies, e.g., bidirectional matching with high-confidence predictions and self-penalization using low-confidence predictions, the models can learn from each other or from its own results. Through our proposed methods, the models gradually transfer domain knowledge from the source to the target domain. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method on three public benchmarks: Office-31, Office-Home, and VisDA-2017
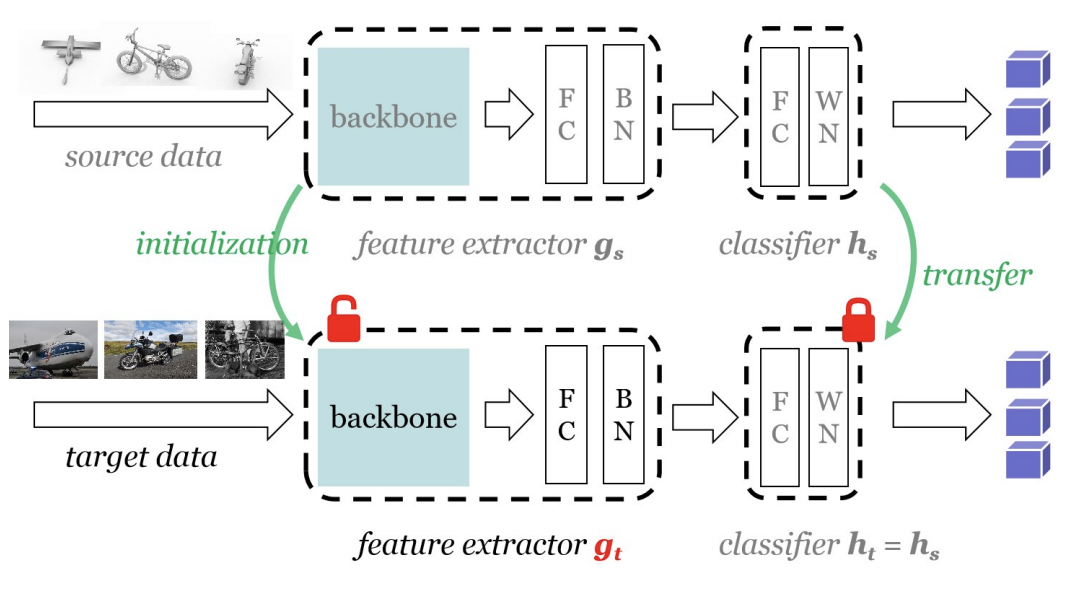
Do We Really Need to Access the Source Data? Source Hypothesis Transfer for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
ICML 2020
Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) aims to leverage the knowledge learned from a labeled source dataset to solve similar tasks in a new unlabeled domain. Prior UDA methods typically require to access the source data when learning to adapt the model, making them risky and inefficient for decentralized private data. This work tackles a practical setting where only a trained source model is available and investigates how we can effectively utilize such a model without source data to solve UDA problems. We propose a simple yet generic representation learning framework, named \emph{Source HypOthesis Transfer} (SHOT). SHOT freezes the classifier module (hypothesis) of the source model and learns the target-specific feature extraction module by exploiting both information maximization and self-supervised pseudo-labeling to implicitly align representations from the target domains to the source hypothesis. To verify its versatility, we evaluate SHOT in a variety of adaptation cases including closed-set, partial-set, and open-set domain adaptation. Experiments indicate that SHOT yields state-of-the-art results among multiple domain adaptation benchmarks.
Continuously Indexed Domain Adaptation
ICML 2020
Existing domain adaptation focuses on transferring knowledge between domains with categorical indices (e.g., between datasets A and B). However, many tasks involve continuously indexed domains. For example, in medical applications, one often needs to transfer disease analysis and prediction across patients of different ages, where age acts as a continuous domain index. Such tasks are challenging for prior domain adaptation methods since they ignore the underlying relation among domains. In this paper, we propose the first method for continuously indexed domain adaptation. Our approach combines traditional adversarial adaptation with a novel discriminator that models the encoding-conditioned domain index distribution. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates the value of leveraging the domain index to generate invariant features across a continuous range of domains. Our empirical results show that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art domain adaption methods on both synthetic and real-world medical datasets.
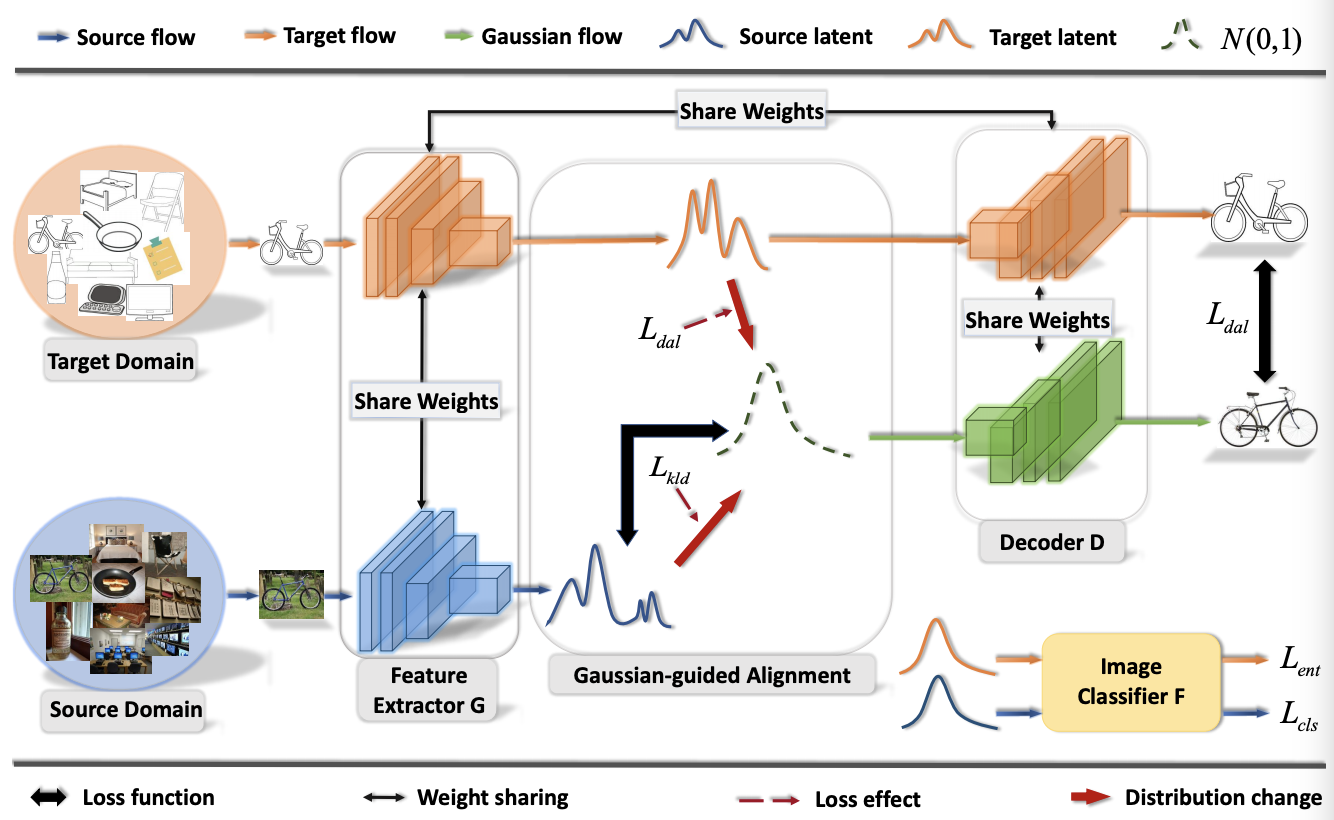
Discriminative Feature Alignment: Improving Transferability of Unsupervised Domain Adaptation by Gaussian-guided Latent Alignment
In this study, we focus on the unsupervised domain adaptation problem where an approximate inference model is to be learned from a labeled data domain and expected to generalize well to an unlabeled data domain. The success of unsupervised domain adaptation largely relies on the cross-domain feature alignment. Previous work has attempted to directly align latent features by the classifier-induced discrepancies. Nevertheless, a common feature space cannot always be learned via this direct feature alignment especially when a large domain gap exists. To solve this problem, we introduce a Gaussian-guided latent alignment approach to align the latent feature distributions of the two domains under the guidance of the prior distribution. In such an indirect way, the distributions over the samples from the two domains will be constructed on a common feature space, i.e., the space of the prior, which promotes better feature alignment. To effectively align the target latent distribution with this prior distribution, we also propose a novel unpaired L1-distance by taking advantage of the formulation of the encoder-decoder. The extensive evaluations on nine benchmark datasets validate the superior knowledge transferability through outperforming state-of-the-art methods and the versatility of the proposed method by improving the existing work significantly.