DualToken-ViT Position-aware Efficient Vision Transformer with Dual Token Fusion
[token attention multimodal convolution light-vit vit deep-learning transformer This is my reading note for DualToken-ViT Position-aware Efficient Vision Transformer with Dual Token Fusion. The paper discuss efficient transformer, which is based on combining convolution with attention: where convolution extracts local information and then fused with global information via attention.

Introduction
However, the quadratic complexity of self-attention renders ViTs computationally intensive, and their lack of inductive biases of locality and translation equivariance demands larger model sizes compared to CNNs to effectively learn visual features. In this paper, we propose a light-weight and efficient vision transformer model called DualToken-ViT that leverages the advantages of CNNs and ViTs. DualToken-ViT effectively fuses the token with local information obtained by convolution-based structure and the token with global information obtained by self-attention-based structure to achieve an efficient attention structure. In addition, we use position-aware global tokens throughout all stages to enrich the global information, which further strengthening the effect of DualToken-ViT. P (p. 1)
Although window self-attention [19] is also able to extract local information, we observe that it is less efficient than the convolution on our light-weight model. To reduce the computational complexity of self-attention in global information broadcasting, we downsample the feature map that produces key and value by step-wise downsampling, which can retain more information during the downsampling process. (p. 2)
Related Works
Efficient Vision Transformers
[31, 6] apply the pyramid structure to ViTs, which will incrementally transform the spatial information into the rich semantic information. To achieve efficient ViTs, some works are beginning to find suitable alternatives to self-attention in computer vision tasks, such as [23, 2], which make the model smaller by reducing the complexity of self-attention. [31, 32, 25] reduce the required computational resources by reducing the number of tokens involved in self-attention. [19, 8] use locally-grouped self-attention based methods to reduce the complexity of the overall attention part. There are also some works that combine convolution into ViTs, for example, [32, 13] use convolution-based FFN (feed-forward neural network) to replace the normal FFN, [25] uses more convolution-based structure in the shallow stages of the model and more transformer-based structure in the deep stages of the model. Moreover, there are also many works that use local information extracted by convolution or window self-attention to compensate for the shortcomings of ViTs, such as [22, 24]. (p. 2)
Efficient Attention Structures
For local attention, convolution works well for extracting local information in vision tasks, e.g., [22, 24] add convolution to model to aggregate local information. Among transformer-based structures, locally-grouped self-attention [19, 8] can also achieve local attention by adjusting the window size, and their complexity will be much less than that of self-attention. For global attention, self-attention [30] has a strong ability to extract global information, but on light-weight models, it may not be able to extract visual features well due to the lack of model size. Methods [14, 5, 35] using global tokens can also aggregate global information. They use self-attention to update global tokens and broadcast global information. Since the number of tokens in global tokens will not be set very large, the complexity will not be very high. Some works [24, 14, 25, 5] achieve a more efficient attention structure by combining both local and global attention. (p. 2)
Methodology
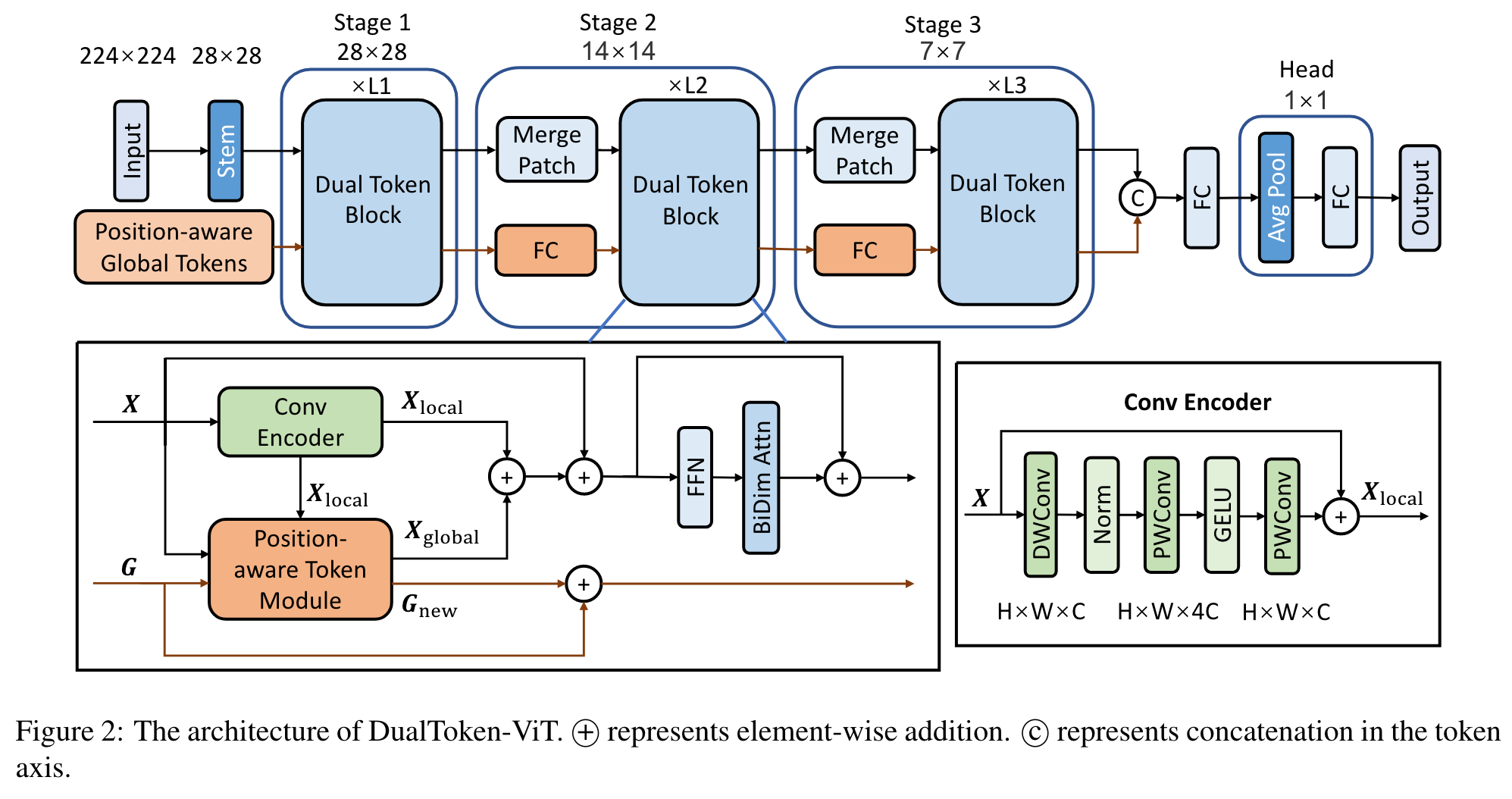
As shown in Figure 2, DualToken-ViT is designed based on the 3-stage structure of LightViT [14]. The structure of stem and merge patch block in our model is the same as the corresponding part in LightViT. There are two branches in our model: image tokens and position-aware global tokens. The branch of image tokens is responsible for obtaining various information from position-aware global tokens, and the branch of positionaware global tokens is responsible for updating positionaware global tokens through the branch of image tokens and passing it on. In the attention part of each Dual Token Block, we obtain information from the position-aware global tokens and fuse local and global information. We also add BiDim Attn (bi-dimensional attention) proposed in LightViT after the FFN. (p. 3)
Fusion of Local and Global Information
Conv Encoder has the same structure as the ConvNeXt block [20], (p. 3)
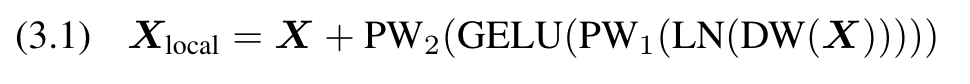
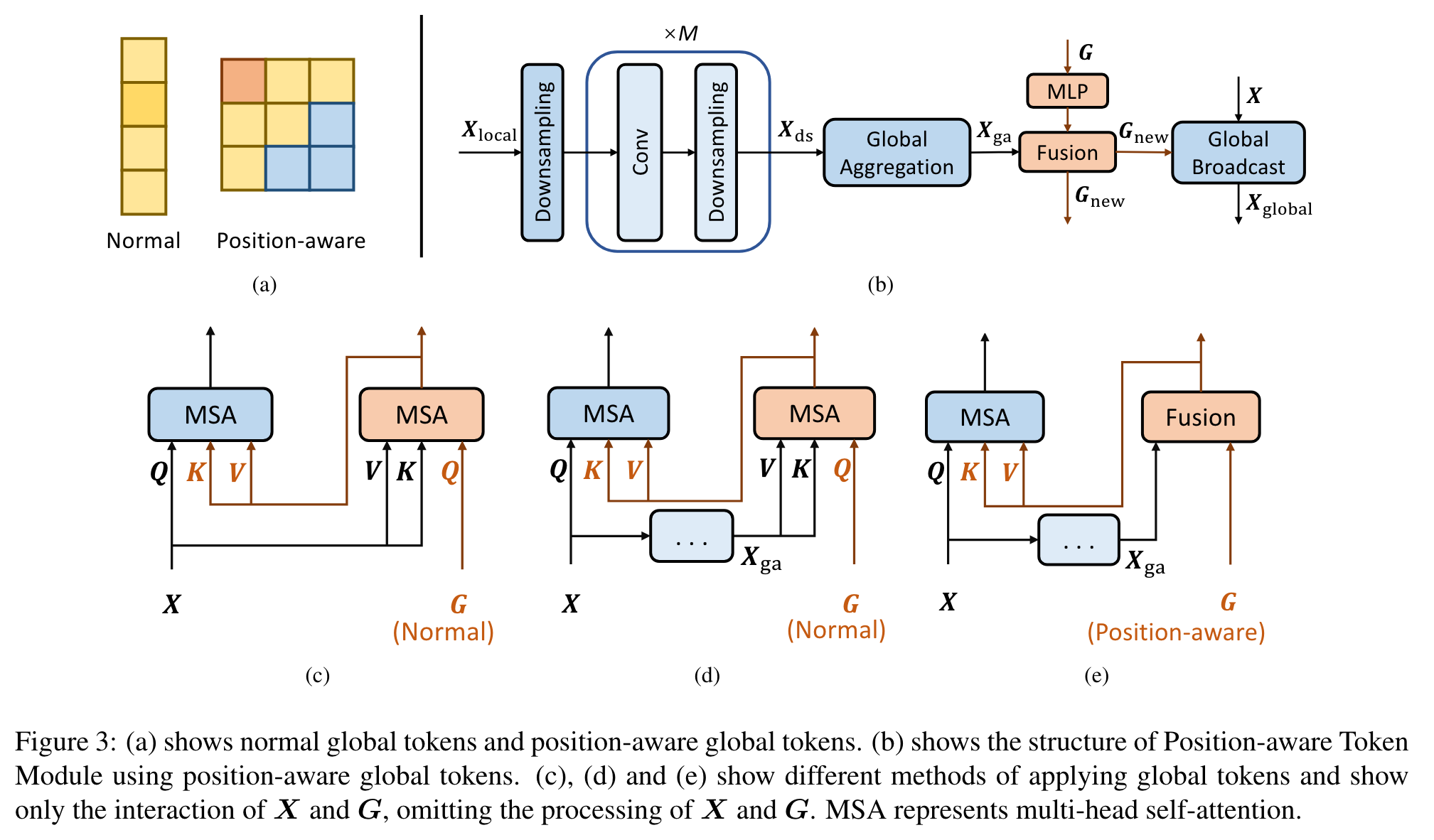
Position-aware Token Module
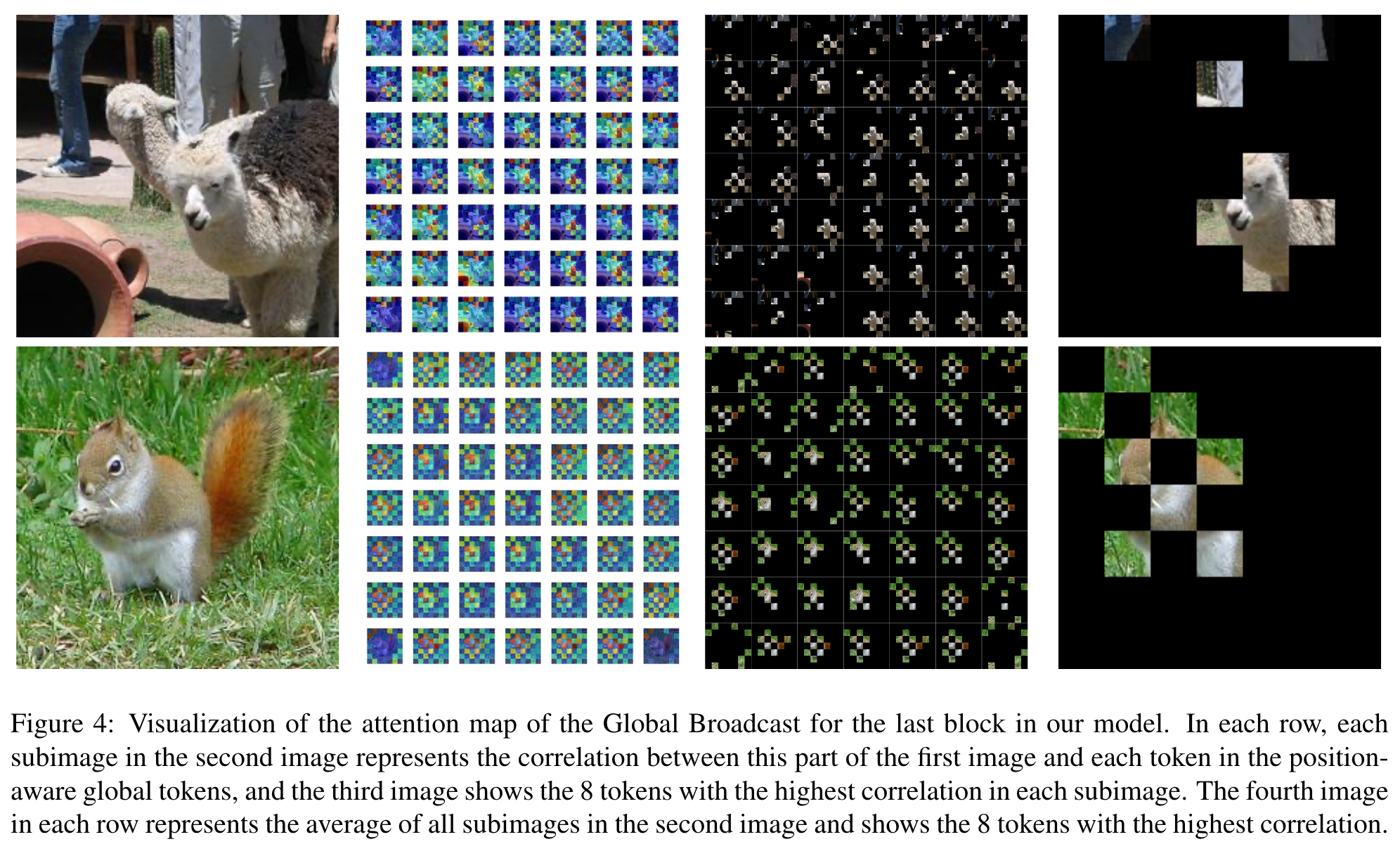
In order to reduce the complexity of extracting global information, we first downsample Xlocal containing local information and aggregate the global information. Position-aware global tokens are then used to enrich global information. We end up broadcasting this global information to image tokens. (p. 3)
After that, local information is extracted by convolution and downsampled twice, and the process is repeated M times until the feature map size reaches the expected size (p. 3)
(2) Global Aggregation. Aggregation of global information using multi-head self-attention for the Xds output in the previous step: (p. 4)
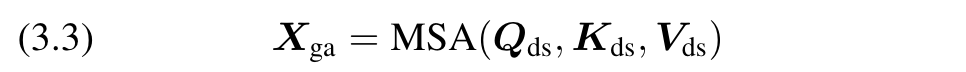
(3) Enrich the global information. Use position-aware global tokens G to enrich Xga’s global information: (p. 4)
(4) Global Broadcast. The global information in Gnew is broadcast to the image tokens using self-attention. This process is represented as follows: (p. 4)
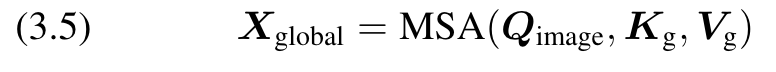
Fusion
Fusing the two tokens, which contain local and global information respectively: (p. 4)
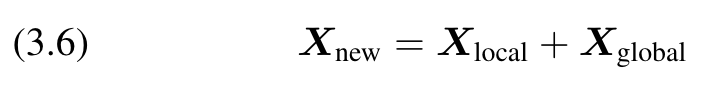
Position-aware Global Tokens
Global Tokens with Position Information
The normal global tokens use the way in Figure 3(c) to fuse X and G via multi-head self-attention and broadcast the global information. Figure 3(e) is our Position aware Global Tokens, which we set to the same number of tokens as in Xga, and use weighted summation to fuse them: (p. 4)
Since the normal MLP is only in the channel dimension, we also attempt to use token-mixing MLP [28] to additionally extract the information in the spatial dimension: (p. 5)
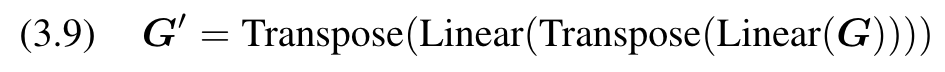
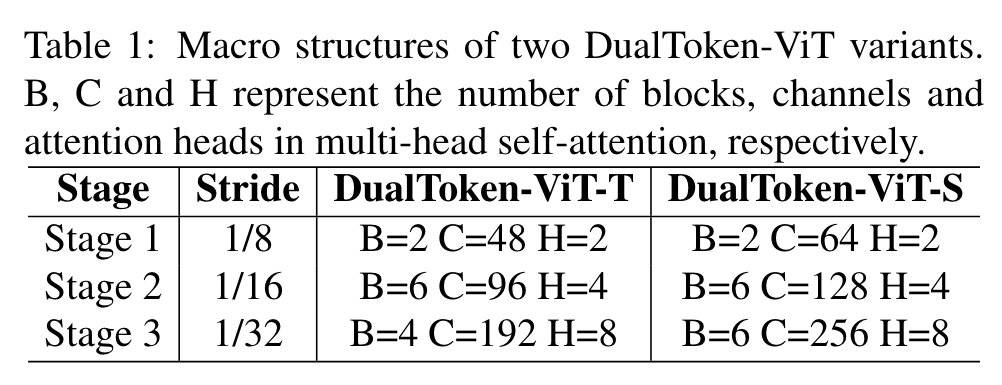
Architectures
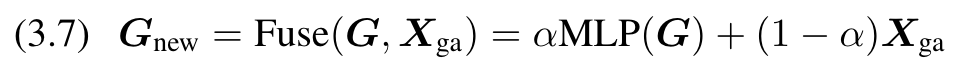
To prevent the complexity of the model from being too large, we set the size of positionaware global tokens to 7×7. (p. 5)
Experiments
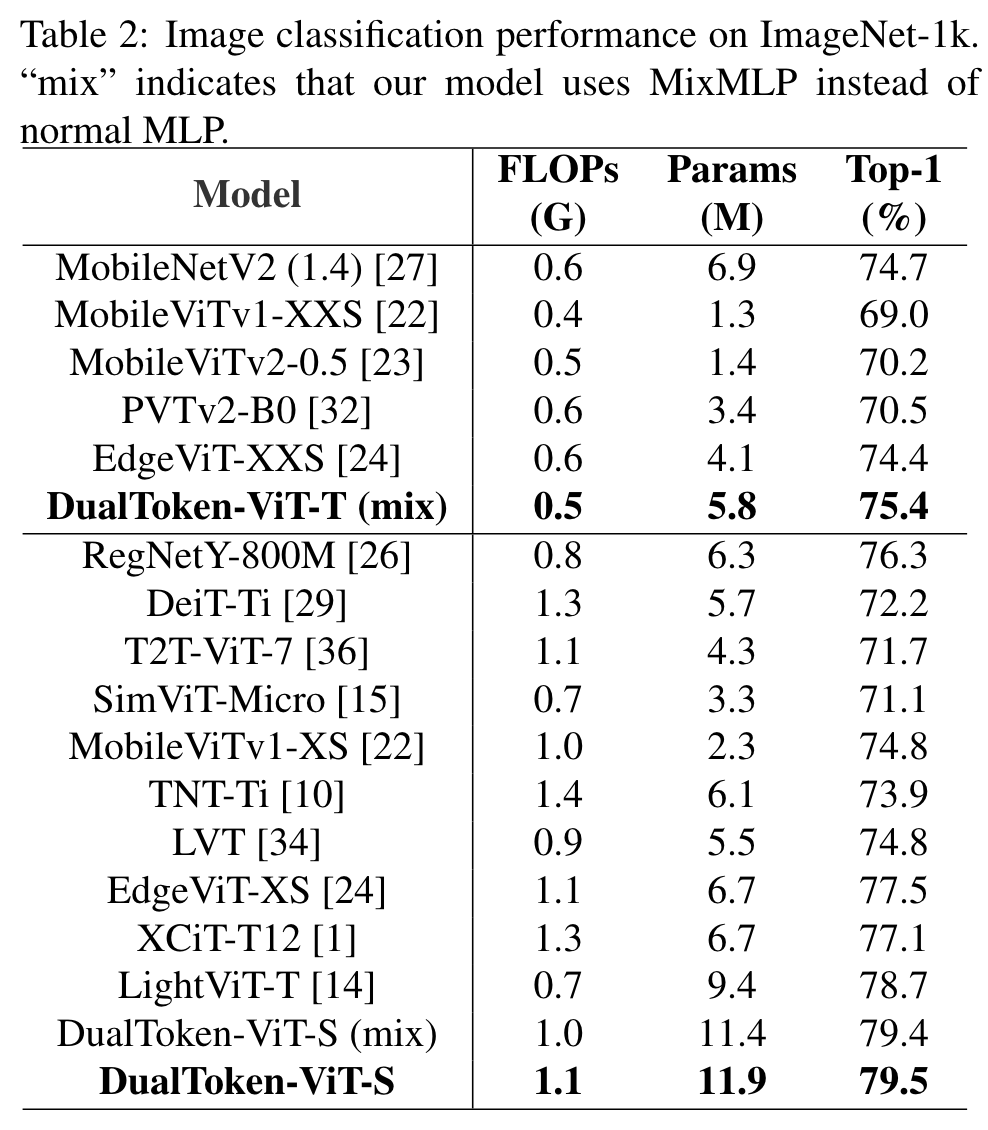
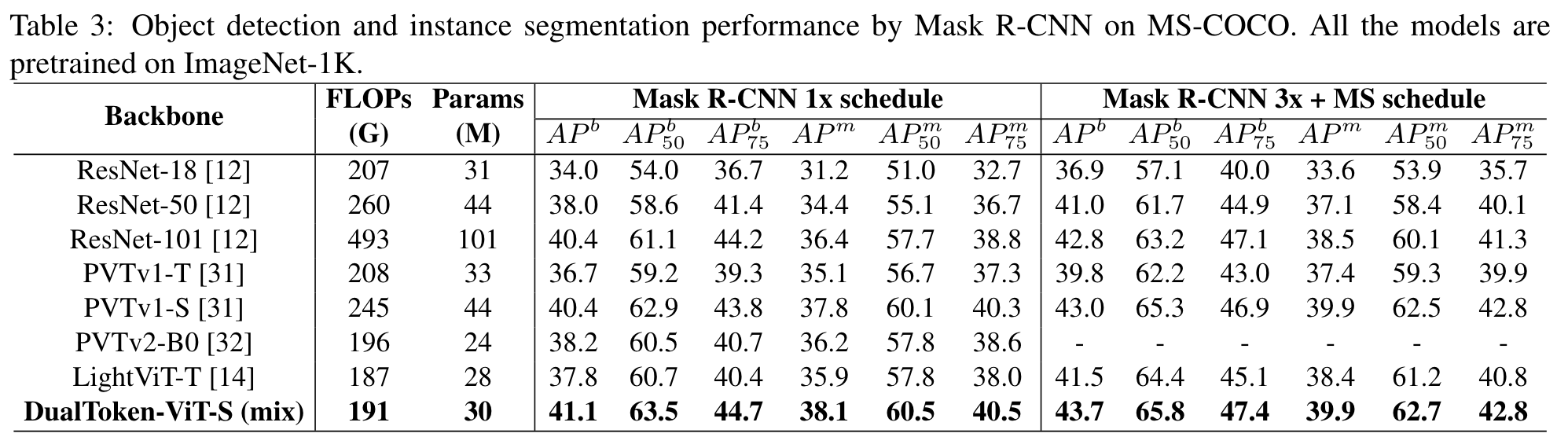
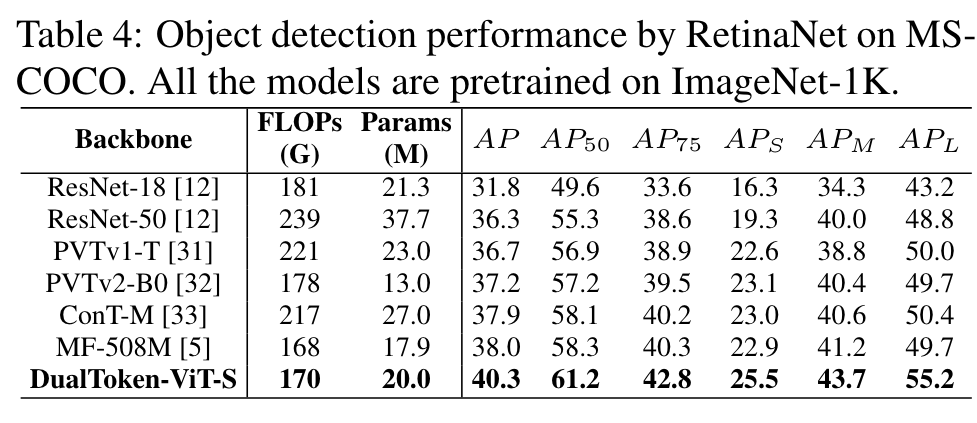
Ablation Study
MLPs
The normal MLP is 0.1% more accurate than MixMLP, but it adds a little extra FLOPs and parameters. (p. 6)
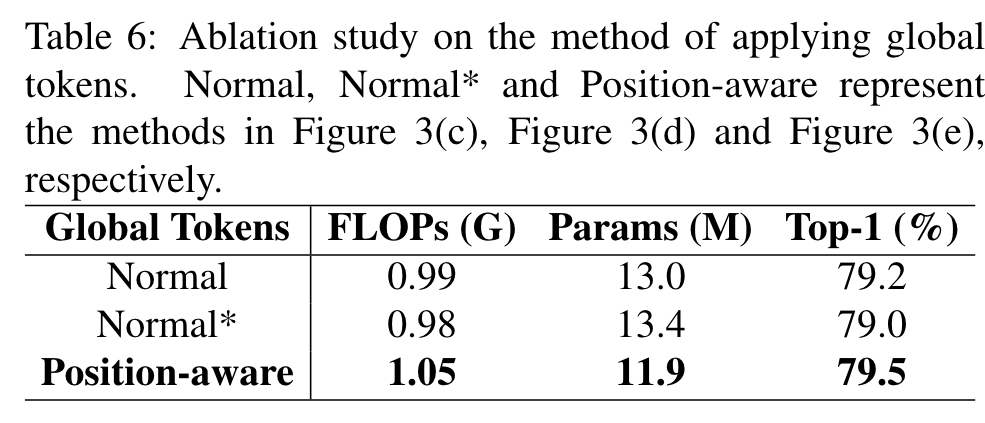
Different methods of applying global tokens
The experimental results are shown in Table 6, which show that our position-aware-based method performs the best and has 1.1M less parameters than the Normal method, with only 0.06G more FLOPs. Since the other two methods employ multi-head self-attention based fusion that requires many parameters, whereas our method employs weighted summation based fusion, our method has the smallest parameters. This demonstrates the superiority of position-aware global tokens. (p. 6)
The number of tokens in position-aware global tokens
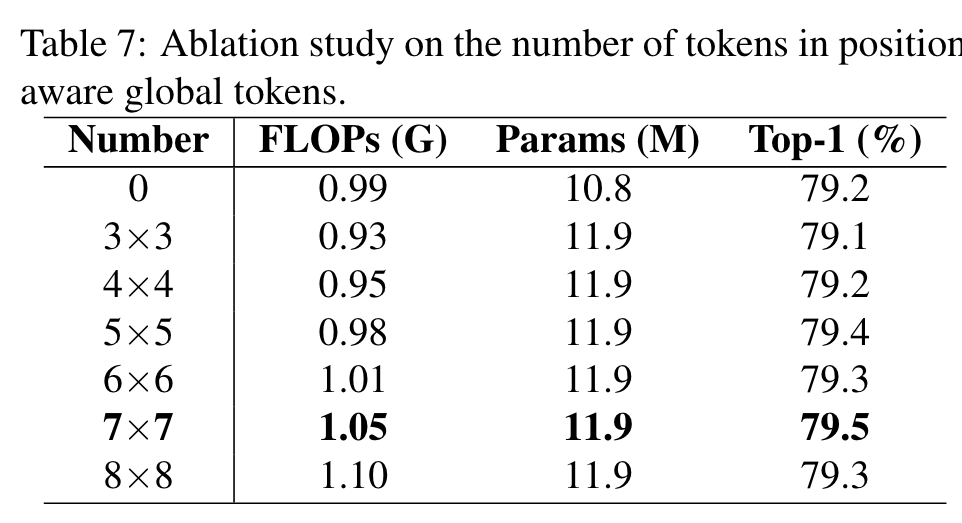
The model with the number of tokens set to 7×7 has the best performance due to the sufficient number of tokens and does not damage the information by the interpolation method. (p. 7)
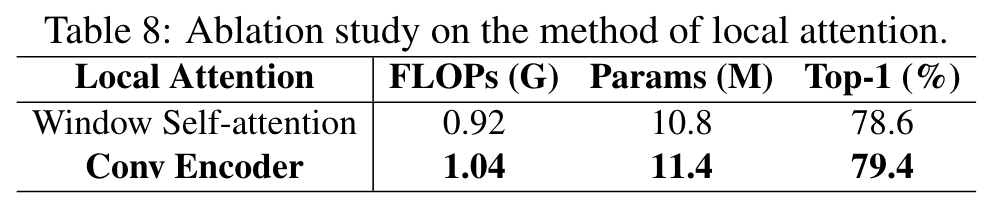
Local attention
The model using Conv Encoder as local attention achieves better performance, with 0.8% more accuracy than when using window self-attention, and the number of FLOPs and parameters does not increase very much. (p. 7)
Downsampling
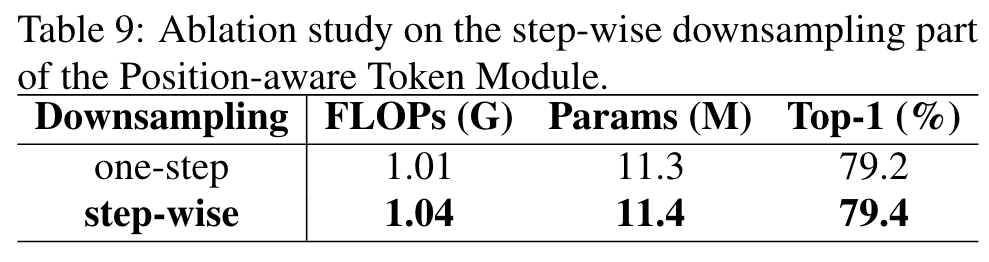
The experimental results on DualToken-ViT-S (mix) are shown in Table 9. Step-wise downsampling is 0.2% more accurate than one-step downsampling, and FLOPs and parameters are only 0.03G and 0.1M more, respectively. (p. 7)
