Effcient Deep Neural Network
[flattened-network xception-network mobilenet factorized-network deep-learning squeezenet mixnet In this post, we will introduce some neural networks which are suitable for running on mobile devices.
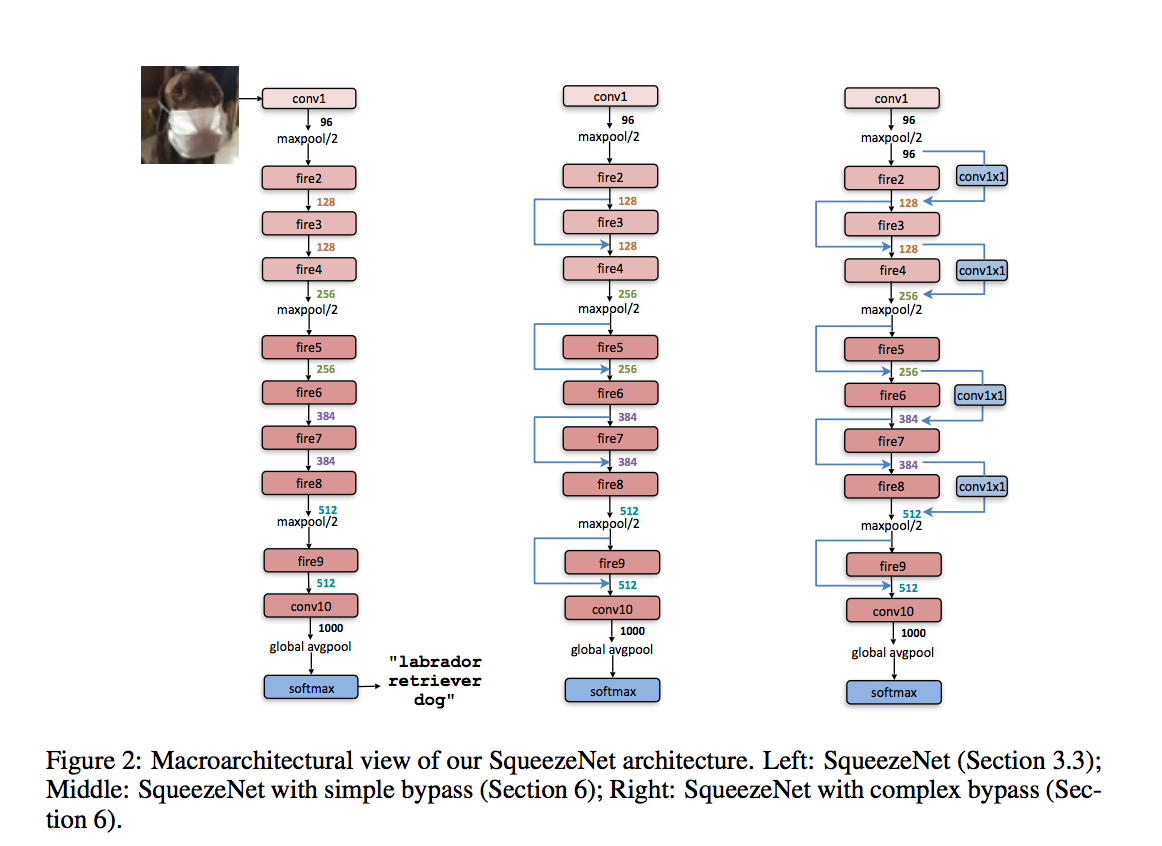
SqueezeNet
SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size
SqueezeNet is one of the first work to reduce the network size and computation cost. It utilizes the following techniques:
- Replace 3x3 filters with 1x1 filters.
- Decrease the number of input channels to 3x3 filters.
- Downsample late in the network so that convolution layers have large activation maps.
It proposes fire module which is comprised of a squeeze convolution layer (which has only 1x1 filters), feeding into an expand layer that has a mix of 1x1 and 3x3 convolution. Bypass is applied cross layers.
Flattened Network
Flattened Convolutional Neural Networks for Feedforward Acceleration
Flattened network identifies the redundancy of parameter of convolution filters and address it via low rank approximation. The convolution can be represented via matrix product as $F \times X$, if the filter can be low rank approximated as $F = A \times B$, then $F \times X = A \times (B \times X))$. Flattened network uses 1D filter. Flattened network uses rank-one filter. The saving computation cost for a filter of size $K_x \times K_y \times M \times N$ for flattened network over standard one would be
\[\frac{K_x \times N + K_y \times N + M \times N}{K_x \times K_y \times M \times N} = \frac{1}{K_y \times M} + \frac{1}{K_x \times M} + \frac{1}{K_y \times K_x}\]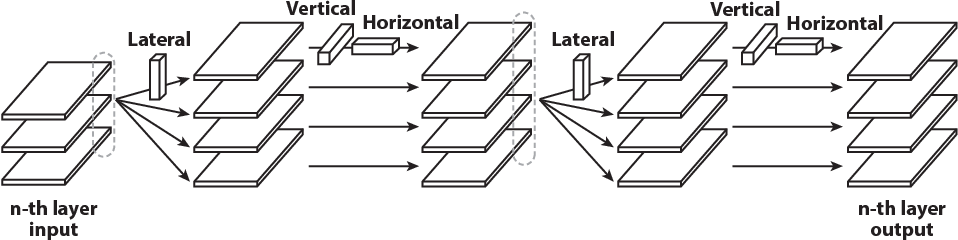
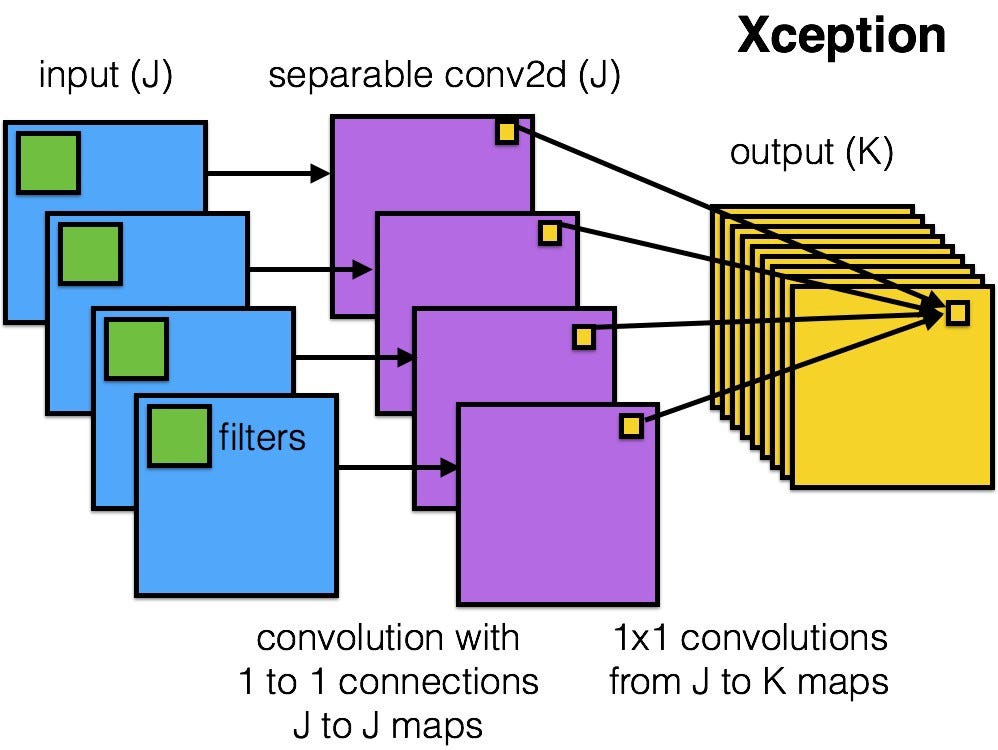
XCeption
Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions
Similar to the idea of MobileNet but working on Inception.
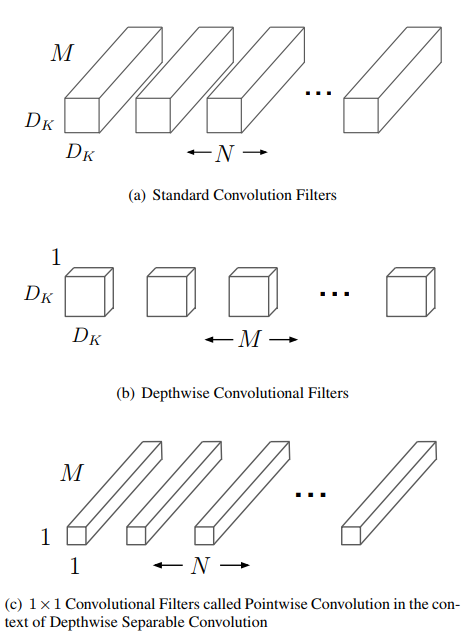
MobileNet
MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications
MobileNet mainly utilizes the separable convolution to reduce the parameter numbers and computational cost. It factorizes the convolution to a pair of depthwise convolution (whose input channel and output channel is one) and pointwise convolution (whose kernel size is 1x1). Depthwise convolution extract spatial information and pointwise convolution combines feature cross channels. For convolution with size $K_x \times K_y \times N$ on input $P \times Q \times M$, the improvement of parameter size and cost for separable convoltuion over standard convolution would be: \(\frac{K_x \times K_y \times M + N \times M}{K_x \times K_y \times M \times N}=\frac{1}{N} + \frac{1}{K_x \times K_y}\\ \frac{P \times Q \times K_x \times K_y \times M + P \times Q \times N \times M}{P \times Q \times K_x \times K_y \times M \times N}=\frac{1}{N} + \frac{1}{K_x \times K_y}\)
MobileNetV2
The difference of MobileNet V2 to V1 is the inverted residual with linear bottleneck. This module takes as an input a low-dimensional compressed representation which is first expanded to high dimension and filtered with a lightweight depthwise convolution. Features are subsequently projected back to a low-dimensional representation with a linear convolution.
Factorized Network
Factorized convolutional neural networks
Factorized network is Similar as MobileNet, but also has the idea of residual network.
MixNet
MixNet finds larger kernel size (up to 9x9) tends to improve the performance on image classification and object detection compared with 3x3 kernel size used in MobileNet V3. As a result, MixNet proposes to have convolution with different kernel size in parallel and combined via concatenation, namely MdConv. MdConv is similar to group wise convolution, where each group has different kernel size.
def mdconv(x, filters, **args):
G = len(filters)
y = []
for xi, fi in zip(tf.split(x, G, axis=-1), filters):
y.append(tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(xi, fi, **args))
return tf.concat(y, axis=-1)
Implementations are already available at Tensorflow and PyTorch
