EventBus in Android lessons learned
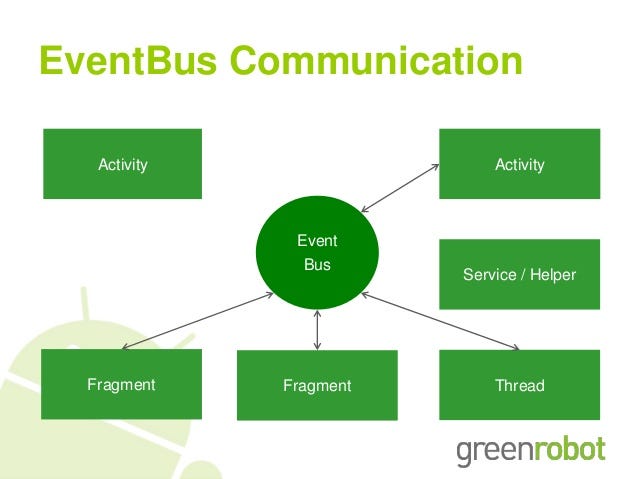
[ ]Event bus can be very helpful when you need to pass events cross multiple objects back and forth. In such cases, the listeners may get messy.
For example, you have object A and B, which need to communicate with each other, then you need to have listeners from A to B and also listeners from B to A. However, image you have more than two objects, you will need o(n^2) listenrs. If you don’t remove all listeners, you will likely to run to memory leak.
With event bus, the life is much easier, where each object only need to register to the event bus to recevice events and post events to event bus:
Pros
- You can effectively decouple your Fragments and Activities and get rid of really complex listener-based architectures.
- The ability to change the receiver thread could be quite useful, specially on Android.
- Is easy to pass small objects in the events for quick UI updates.
Cons
- Is really easy to abuse it and make your code unreadable and untestable.
- You need to fill your code with as many onEvent methods as receivers you want, making it less easy to understand for new people.
- You loss control over who’s notifying who unless you use external plugins.
Go to EventBus in Android: lessons learned to read more.
Written on August 18, 2017