Residual Parameter Transfer for Deep Domain Adaptation
[resnet-50 rank domain-adaption deep-learning lenet office minist group-lasso This is my reading note for Residual Parameter Transfer for Deep Domain Adaptation, which is for domain adaption. Different from existing methods, which mostly aims to learn a network to adpat the (feature) of target domain to the source domain, this paper learns a transform on the parameters of network trained on source domain to the network for the target domain.
The figure belows shows summary of the proposed method. The proposed relies on the parameter transfer to build a network for the target domain from the source domain. Both target domain and source domain will share the same classifier, which is learned from source domain. The source network is first trained with source domain only (left), then fine tuned with data from source domain and target domain (middle).
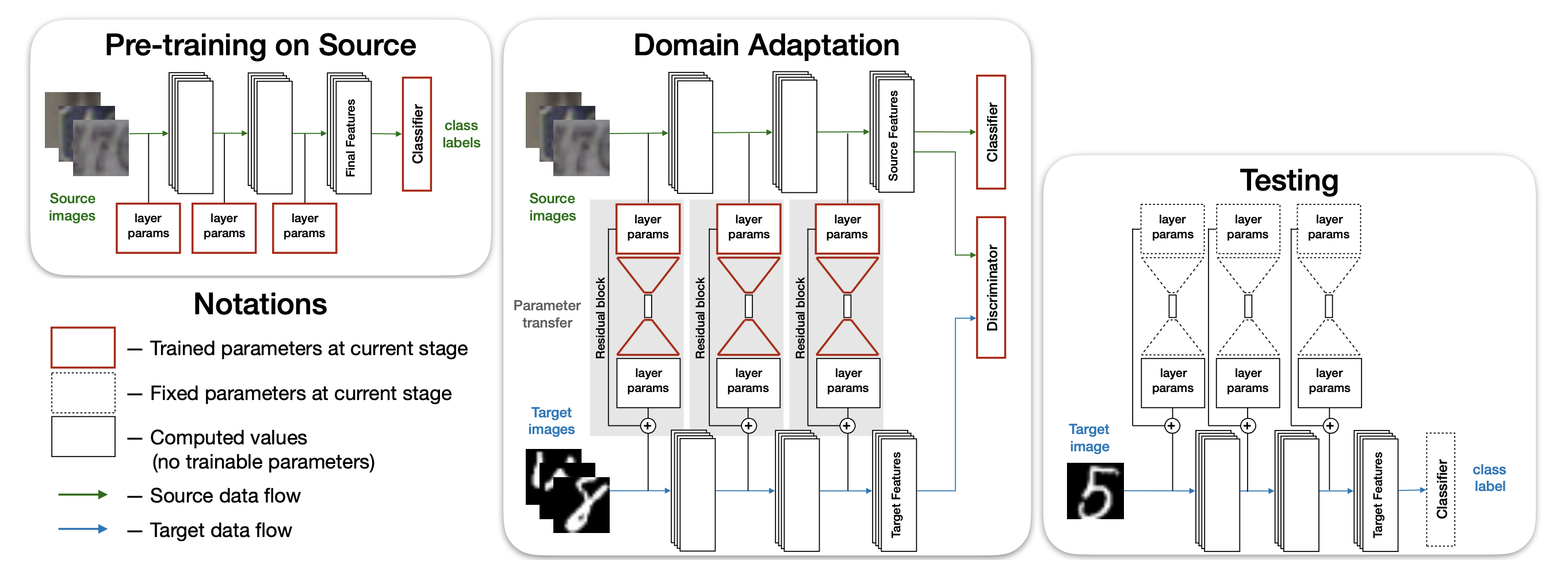
This figure shows an example of the proposed method on digit recognition basde on LeNet, where the parameters of target network is computed from source network, via the residual transform.
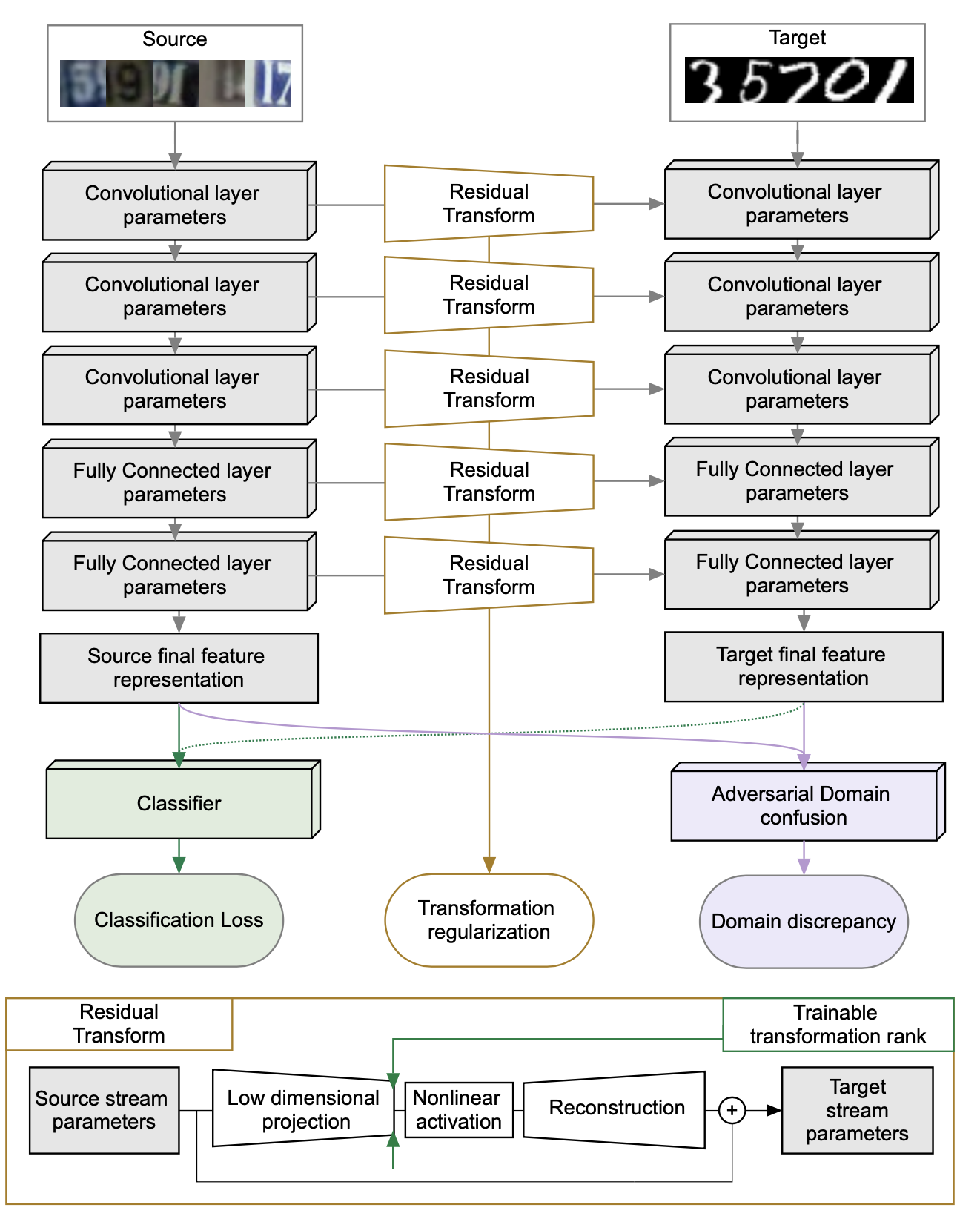
Residual Transform
The residual transform learns a transform for parameter of source network to target network. The proposed method assumes the source network and target network shares the same architecture.
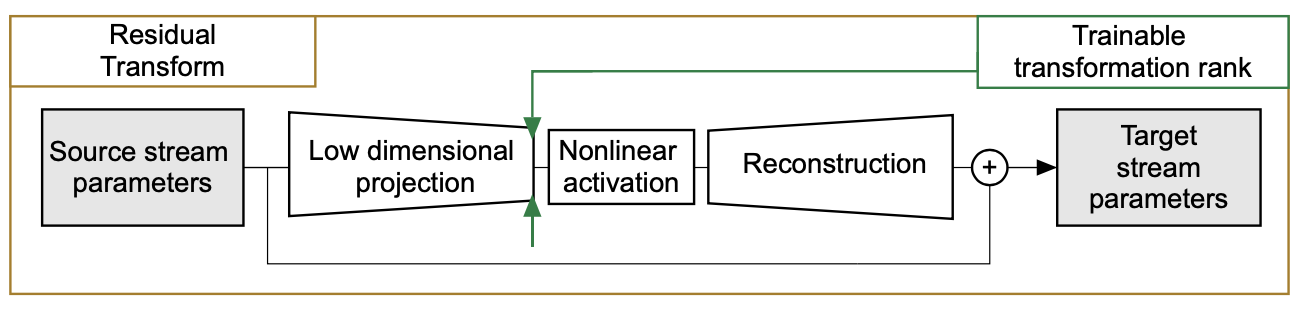
More specifically, the proposed method uses encoder-decoder for residual transform (as shown above), which could be written as:
\[\Theta_i^t=\mathcal{B}_i^1\sigma((\mathcal{A_i^1}^T\Theta_i^s\mathcal{A}_i^2+\mathcal{D}_i)(\mathcal{B}_i^2)^T)+\Theta_i^s\]where \(\Theta_i^s\) and \(\Theta_i^t\) are the parameter for i-th layer of source network and target network accordingly, \((\mathcal{B}_i^1,\mathcal{B}_i^2,\mathcal{A}_i^1,\mathcal{A}_i^2,\mathcal{D}_i)\) are the parameter for the residual transform.
Here the layers parameter as in the matrics form:
- for fully connected layer, \(\Theta_i^s\in\mathbb{R}^{N_{out}\times(N_{in}+1)}\)
- for convolution layer, \(\Theta_i^s\in\mathbb{R}^{N_{out}\times(N_{in}\times k_x\times k_y)}\)
\(\mathcal{T}_i=\mathcal{A_i^1}^T\Theta_i^s\mathcal{A}_i^2+\mathcal{D}_i\in\mathbb{R}^{l_i \times r_i}\) defines the complexity of this transform, which is regularized by \(\ell_{2,1}\) loss and \(\ell_{1,2}\) loss (i.e., group lasso). Group lasso encourages the entire row or column of \(\mathcal{T}_i\) to be zero.
Loss Functions
The following loss functions are used:
- classificaiton loss: standard cross entropy loss is used, applied for source domain only;
- discreprancy loss: measures the similarity of the feature output by source network and target network. Advserial loss is used here, which classifies the feature into source domain and target domain;
- stream loss: to prevents network from learning trivial solutions, e.g., all 0 or source parameter and target parameter are too different from each other.
- rank minimizing term as described in the section.
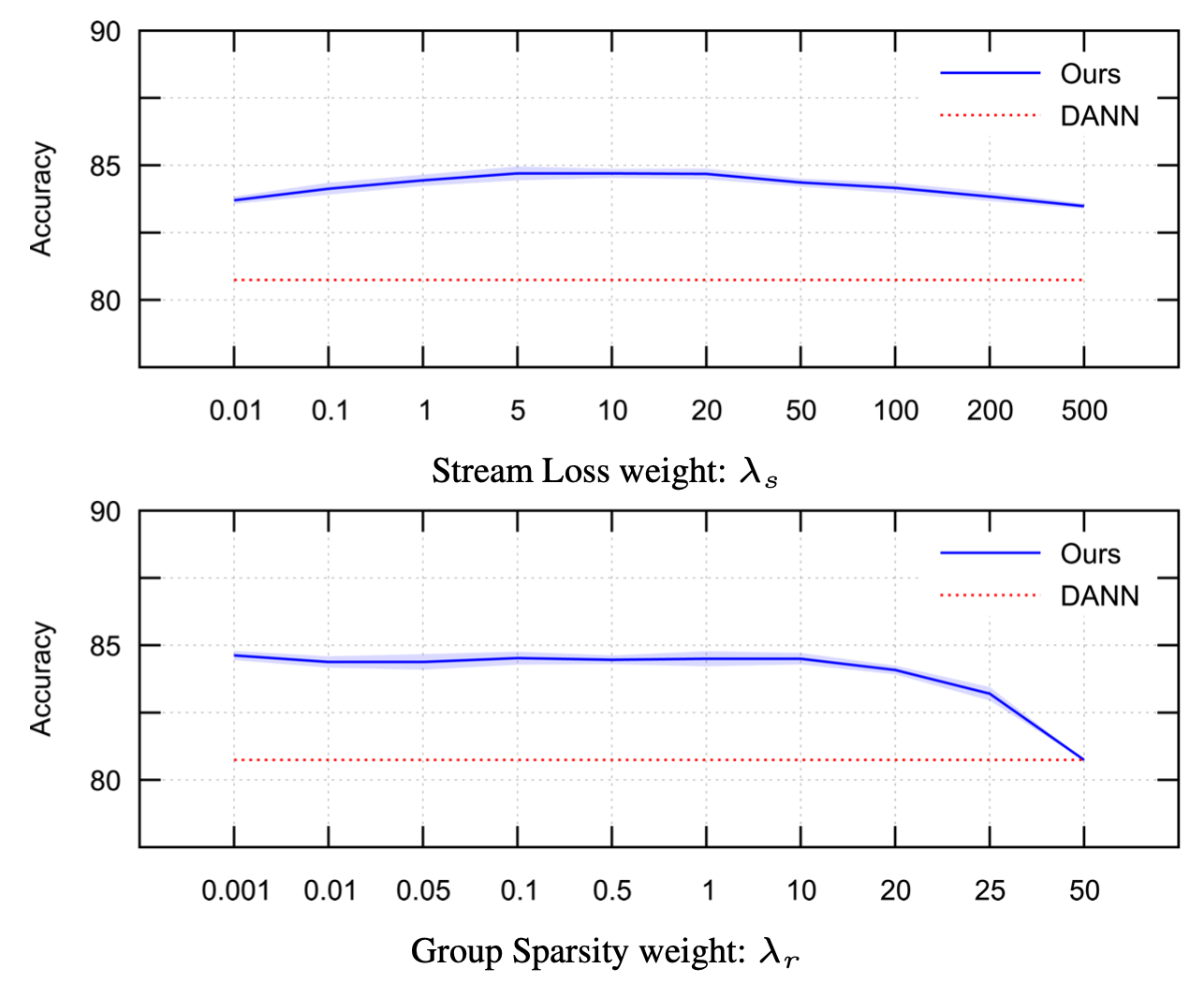
For stream loss, it is implemented as \(\lambda_s(\mathcal{L}_w-\mathcal{Z}(\mathcal{L}_w))\) with \(\mathcal{L}_w=\sum_i{\lVert\mathcal{B}_i^1\sigma((\mathcal{A_i^1}^T\Theta_i^s\mathcal{A}_i^2+\mathcal{D}_i)(\mathcal{B}_i^2)^T)\rVert_{fro}}\). \(\mathcal{Z}\) is the barrier function and log is used. Stream loss is is smallest when \(\mathcal{L}_w=1\) and goes to infinity when \(\mathcal{L}_w\) becomes either very small or very large.
As shown in the image below, the performance is not very sensitive to the weights of those loss functions.
Implementations
The paper uses approximal gradient descent to learn the network:
- use Adam for a pre-defined number of iterations to learn the network without the rank minimizing terms;
- find the approximation to the network learned from previous step, with the rank minimizing terms.
Experiment Results
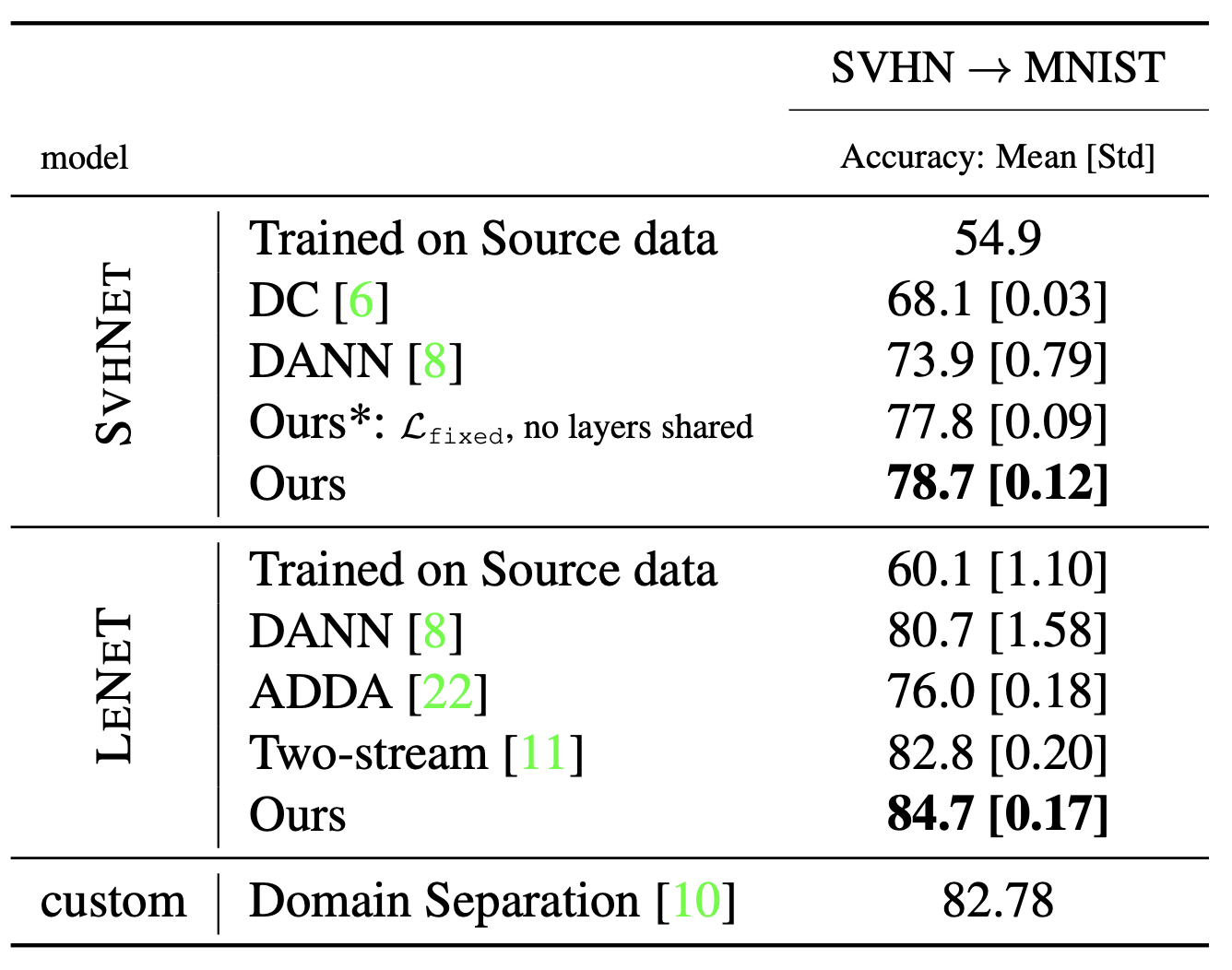
The experiment result on digit recognition from SVHN to MNIST. Here LeNet or SvhNet is used which are very small networks.
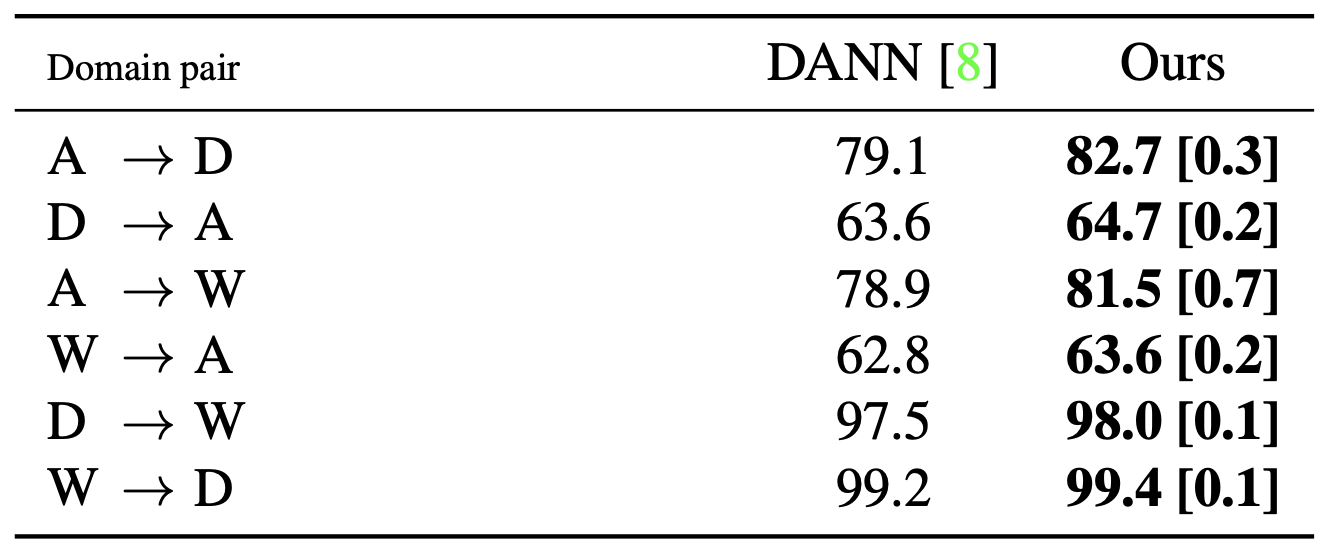
The figure below shows experiment result on object recognition for office dataset with ResNet-50 as network backbone. Please check the asymmetric improvement on A to D (or W) vs D (or W) to A.
Sample images from the Office dataset.
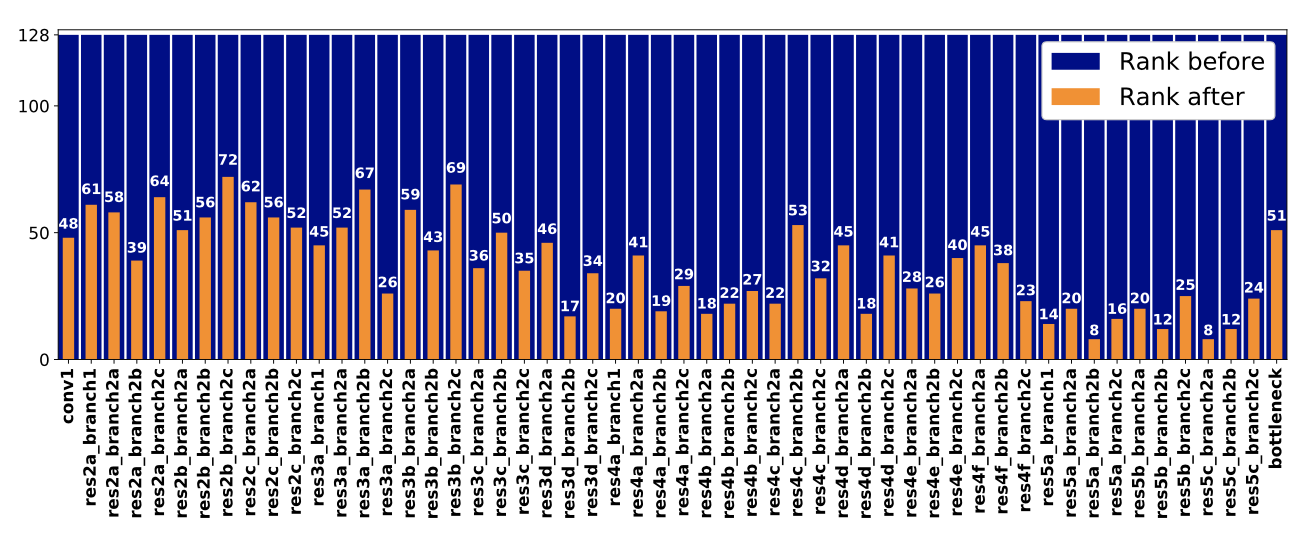
The figure below shows the \(l_i\) and \(r_i\) for the residual transform for ResNet-50 learned on office dataset.