Self Supervised Learning Reading Note
[byol simpleclr dion cvpr self-supervise tutorial contrastive-learning deep-learning 2021 bownet teacher-student obow simsiam This is my reading note on CVPR 2021 tutorial on self supervised learning: Leave Those Nets Alone: Advances in Self-Supervised Learning and Data- and Label-Efficient Learning in An Imperfect World.
Over the last few years, deep learning-based methods have achieved impressive results on image understanding problems. However, real-world vision applications often require models that are able to learn with few or no annotated data. An important and active research approach for achieving this goal is self-supervised / unsupervised learning. Indeed, the last two years there has been a lot of exciting progress in this area, with many new self-supervised pre-training methods managing to match or even surpass the performance of supervised pre-training.
Generative vs Discriminative
Self supervised learning aims to learn a model from unlabled data. It could divided into two groups:
-
generatitve modeling: generate or otherwise model pixels in the input space, examples Autoencoder, Generative Adversarial Networks
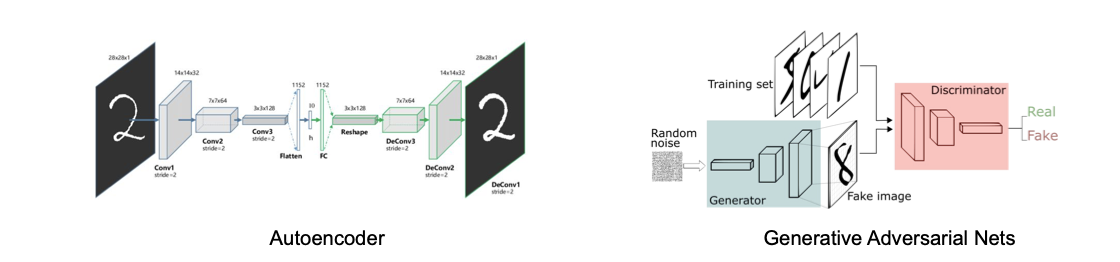
-
Discriminative modeling: train networks to perform pretext tasks where both the inputs and labels are derived from an unlabeled dataset. Heuristic-based pretext tasks: colorization, relative patch location prediction, solving jigsaw puzzle, rotation prediction.
Input Space vs Feature Space
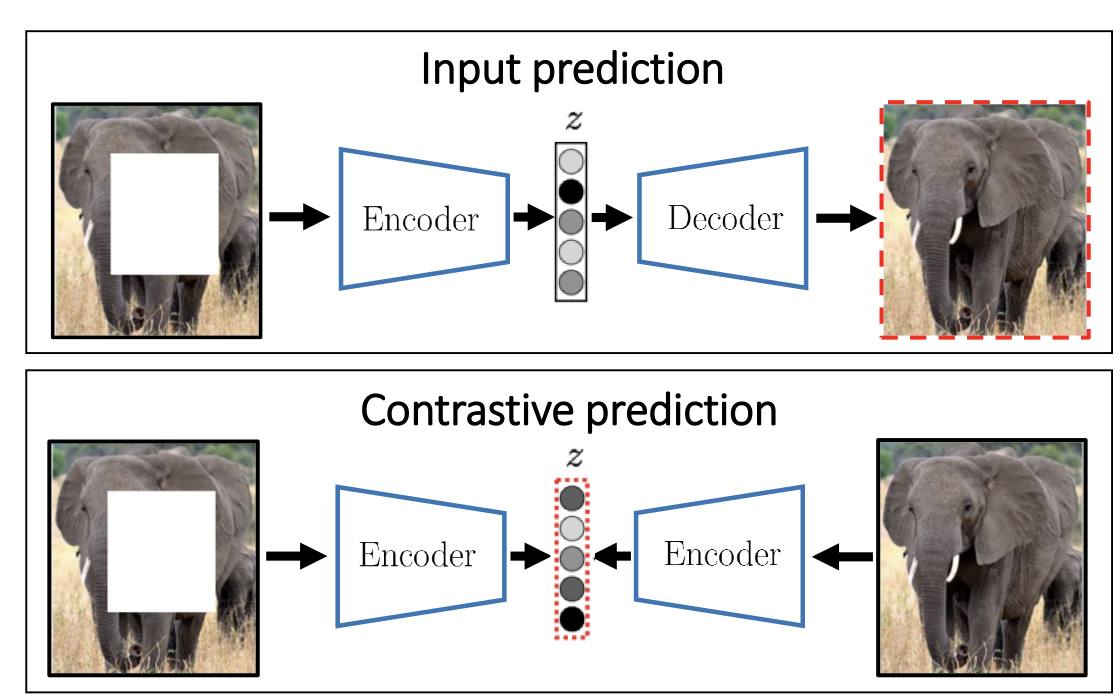
Input Reconstruction
Perturb an image and then train a network to reconstruct the original version. Intuition is to do that the network must recognize the visual concepts of the image . It is one of the earliest methods for self-supervised representation learning.
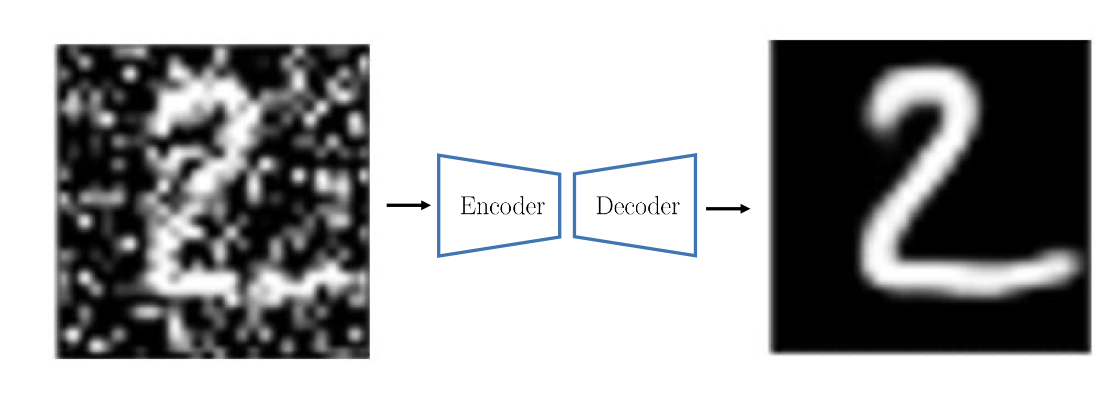
Limitations: input reconstruction is too hard and ambiguous and effort spent on “useless” details: exact color, good boundary, etc. Does not necessarily lead to features good for image understanding tasks.
Feature Reconstruction
Instead of trying to reconstructing the input data, the other methods focus on reconstructing high-level visual concepts rid of “useless” image details.
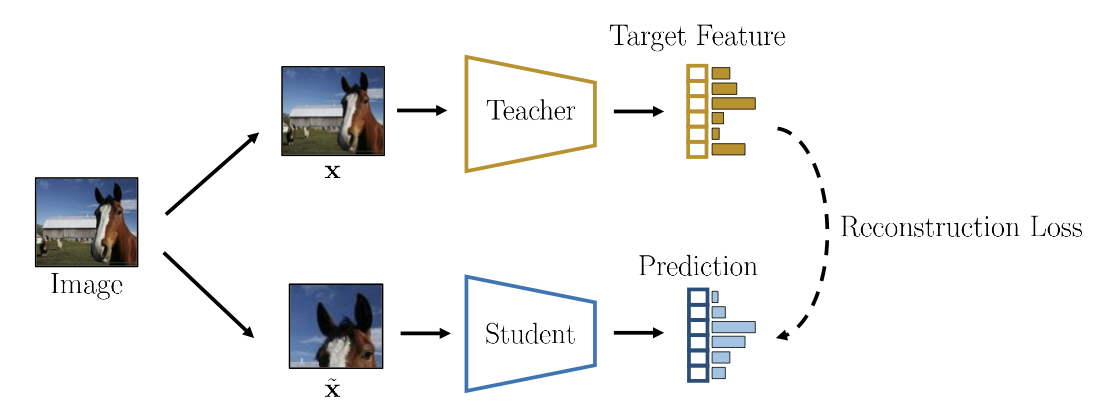
Teacher-Student Methods
The goal here is to distill the knowledge of a pre-trained teacher into a smaller student. Student is trained to predict the teacher target when given the same input image. It also referred as knowledge distillation. Teacher-student methods could be used for self-supervised learning.
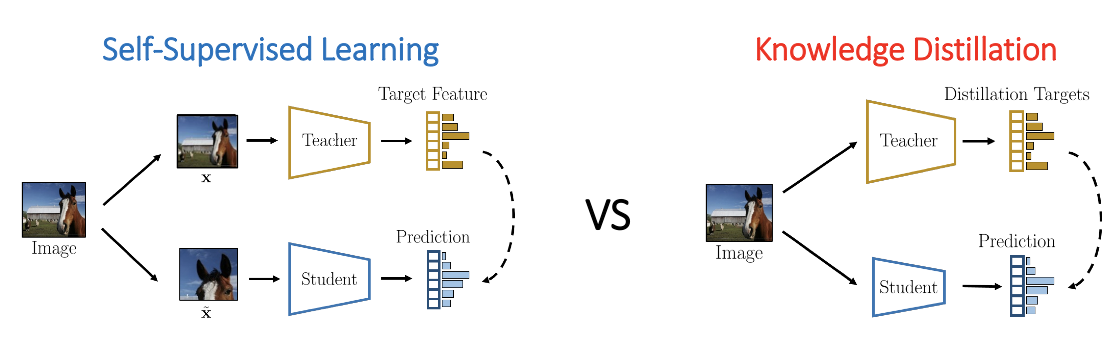
However, where could we find the a good quality teacher?
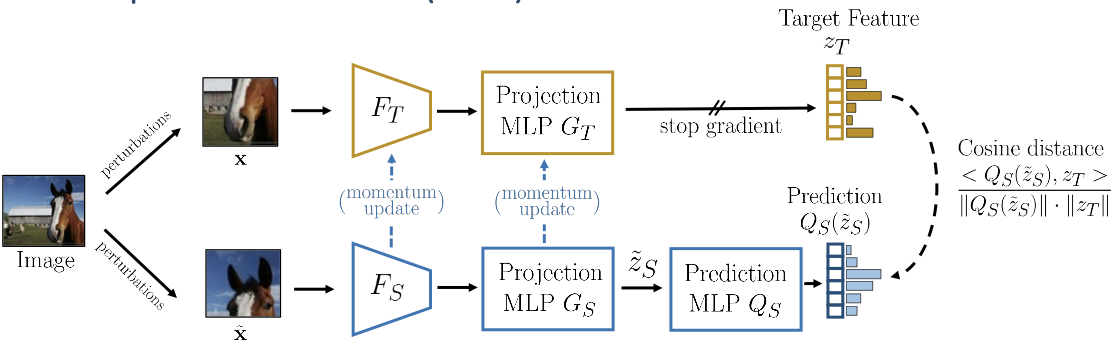
Bootstrap Your Own Latent (BYOL)
BYOL keeps update the teacher as exponential moving average of the student. Notes, the stop gradient for the teacher branch is critical–otherwise your feature will collapse.
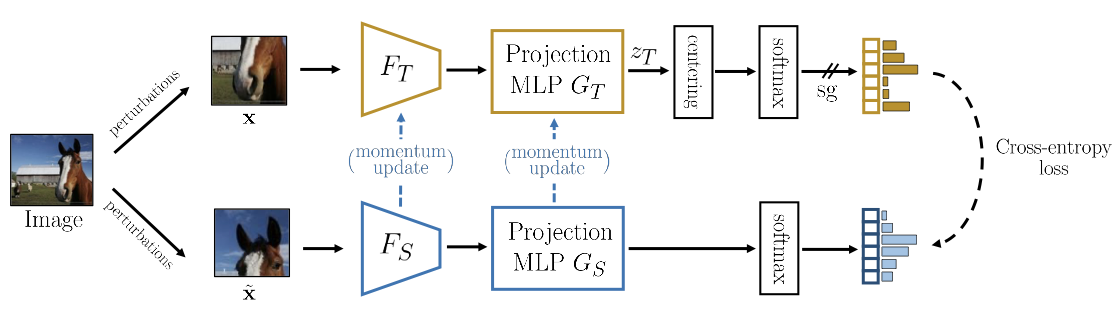
DINO
The novelty of DINO is appyling centering by subtracting the mean feature to prevent collapsing to constant 1-hot targets, then sharpening by using low softmax temperature: prevents collapsing to a uniform target vector.
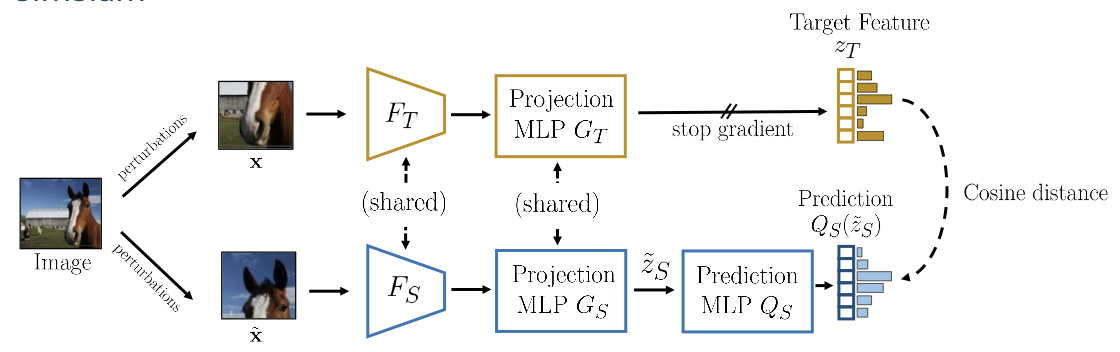
SimSiam
Instead of updating the teacher from student. SimSiam simples make the teacher and student share the same network.
BoWNet
BoWNet utilizes the bag of words ideas to align the feature space.
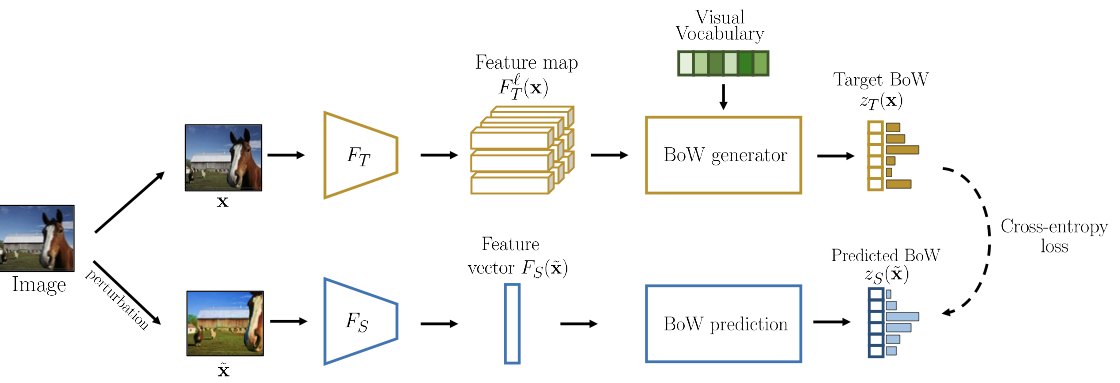
- Teacher: extract feature maps + convert them to Bag-of-Words (BoW) vectors
- Student: must predict the BoW of an image, given as input a perturbed version
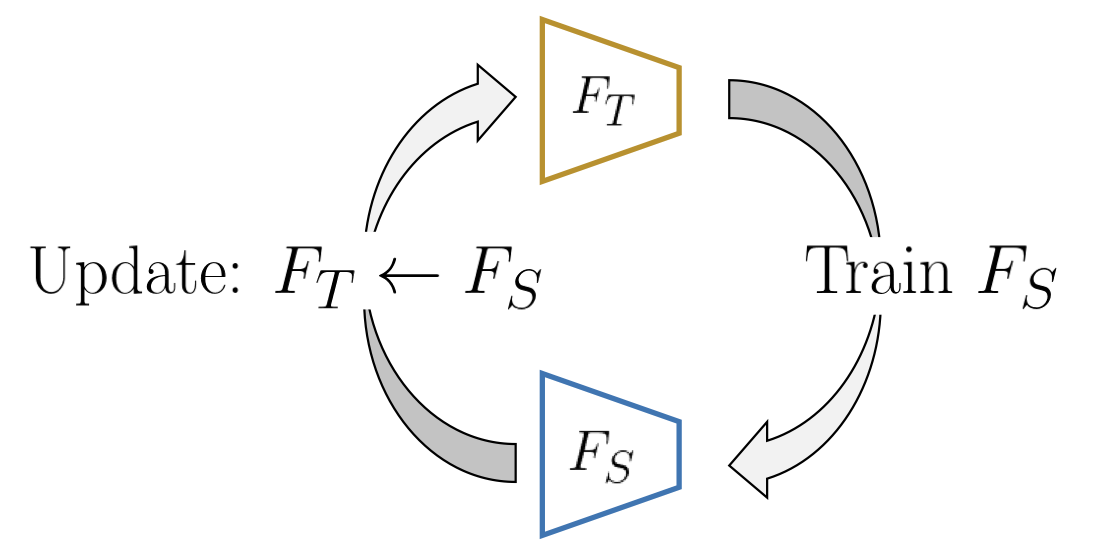
The teacher networks is trained from predicting rotation of images. Students will be trained until convergence, then the teacher will be updated from student; repeat this process.
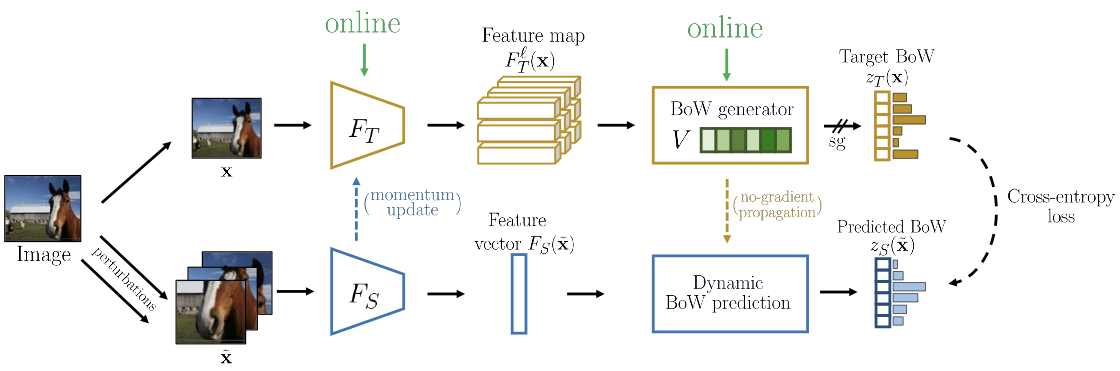
OBoW
In OBoW, the teacher model is updated via exponential moving average of student.
Contrastive Learning
The other group of methods utilize contrastive loss to avoid feature collapse during self supervised learning–for positive samples, pull their features together and for negative samples, push their features away. Constrast learning could be formulated as special type of teacher-student model–teacher and student share the same network like SimSiam.
One example is SimpleCLR : maximizing the agreement of representations under data transformation (e.g., random crop, coloring), using a contrastive loss in the latent/feature space. It reported 10% relative improvement over previous SOTA (cpc v2), outperforms AlexNet with 100X fewer labels.
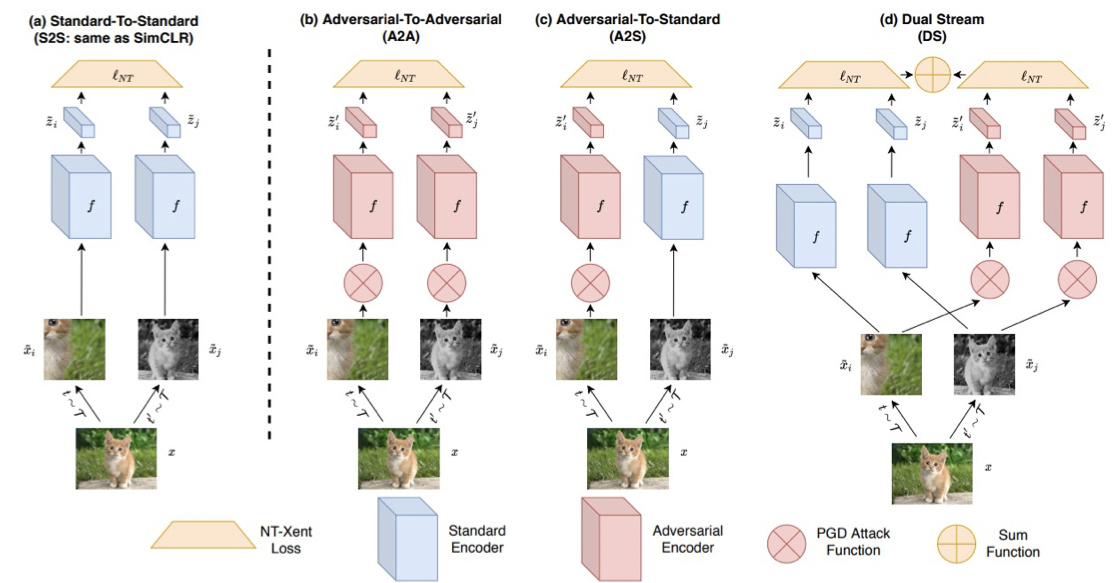
Limitation of Contrastive Learning
Many constrastive learning methods rely on the assumption that, applying the transform shouldn’t change the target label and then the feature representation. This is especially true for ImageNet–there is only a single dominant object in the image.
It has been found, larger objects suppress the learning of smaller objects. The other limitation of constrast learning is that, it requires negative examples, to contrast with postive examples.
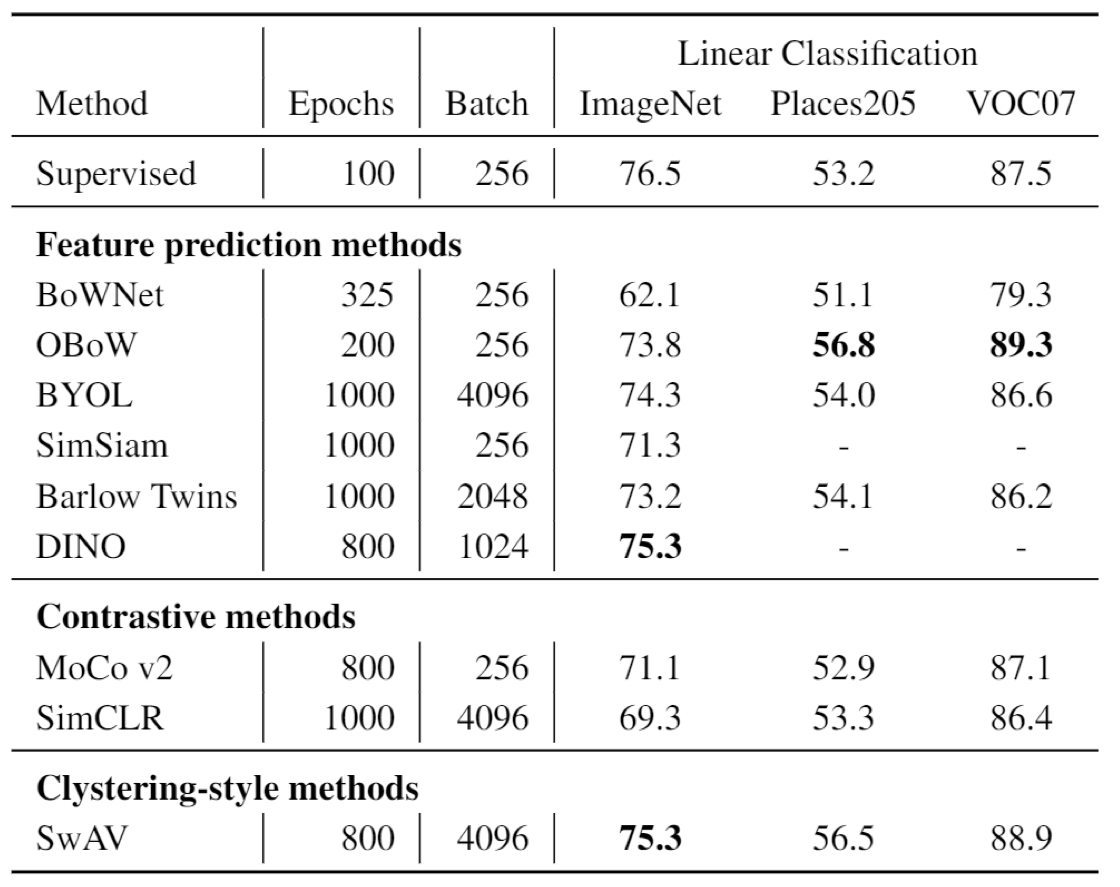
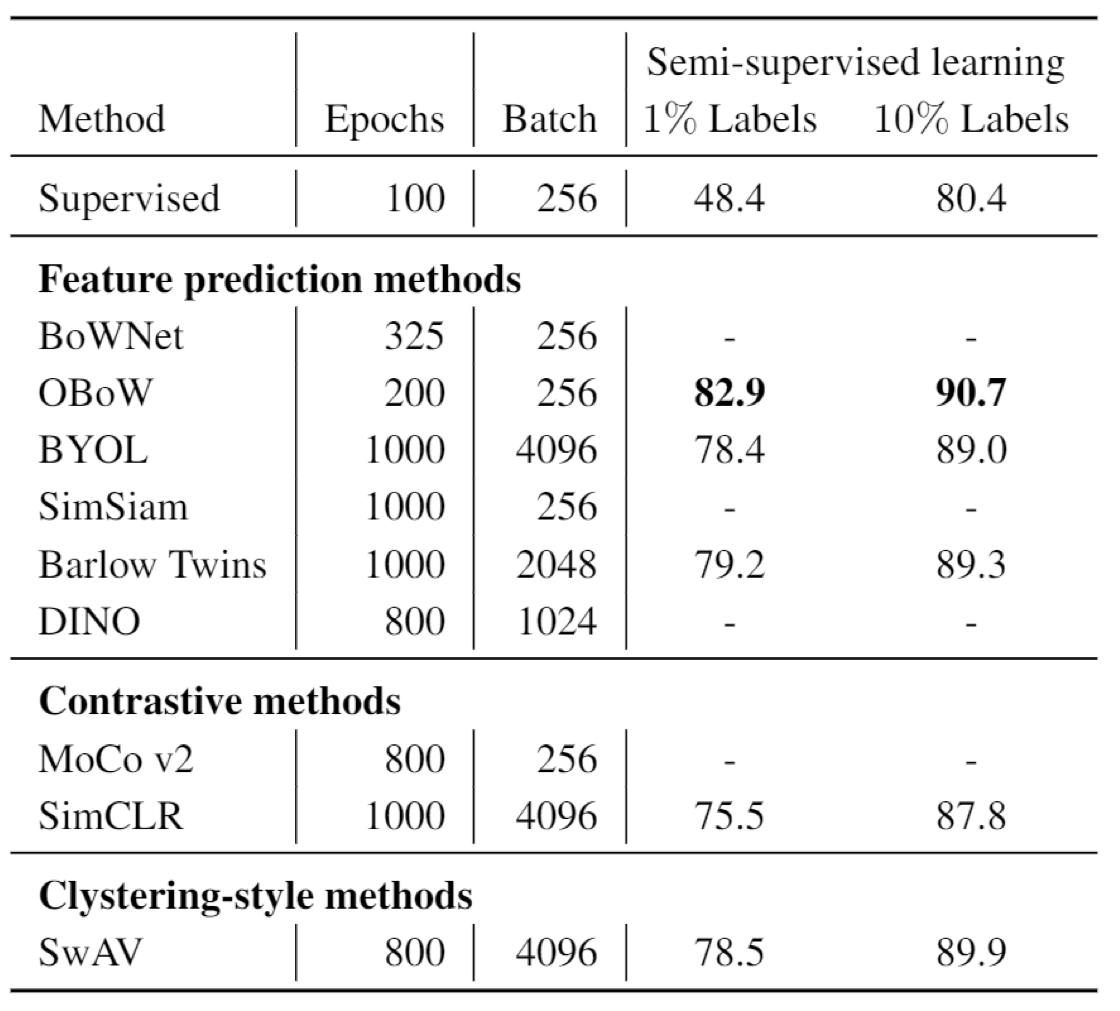
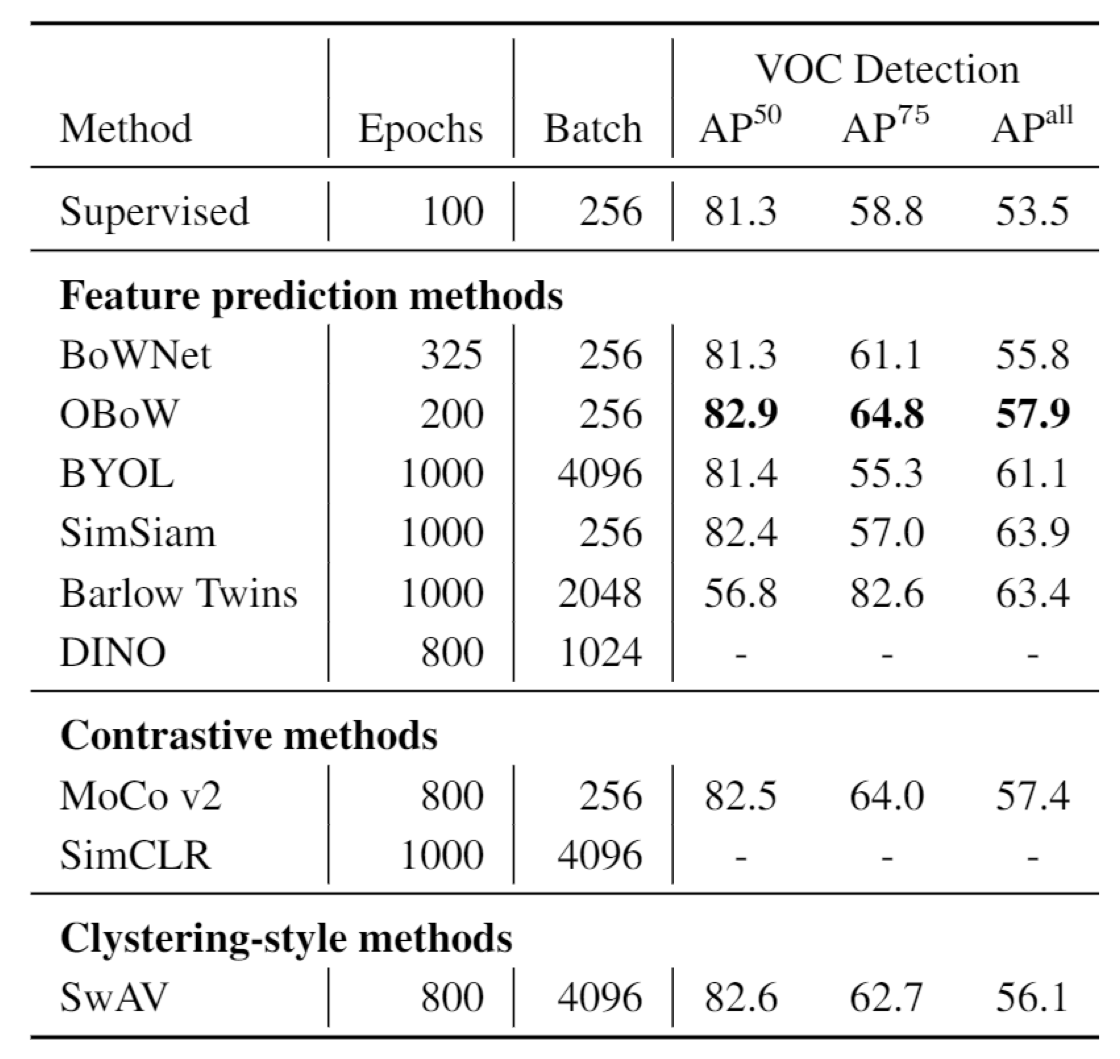
Result
You may find self supervised method could even outperform the supervised methods in image classificaiton and object detection, across several different datasets. The best approach seems to be OBoW.
How to Use Self-Supervised Learning
There are two ways of using self-supervised learning:
-
pre-train the model with self-supervised learning, then fine tune it for your own task;
-
use self-supervised learning as additional task/loss of your own task.
