Graph Database
[system-design graph-database neo4j arangodb orientdb 
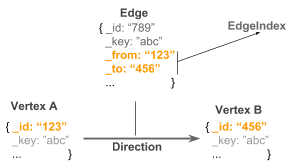
Graph databases are NoSQL databases which use the graph data model comprised of vertices, which is an entity such as a person, place, object or relevant piece of data and edges, which represent the relationship between two nodes.
Graph databases are particularly helpful because they highlight the links and relationships between relevant data similarly to how we do so ourselves.
The underlying storage mechanism of graph databases can vary. Some depend on a relational engine and “store” the graph data in a table (although a table is a logical element. Others use a key-value store or document-oriented database for storage, making them inherently NoSQL structures. Most graph databases based on non-relational storage engines also add the concept of tags or properties, which are essentially relationships having a pointer to another document. This allows data elements to be categorized for easy retrieval en masse.
In the follow sections, we will introduce some of the implementations which are still actively maintained.
Neo4J
Recommend for graph database
Open source, supports ACID, has high-availability clustering for enterprise deployments, and comes with a web-based administration tool that includes full transaction support and visual node-link graph explorer; accessible from most programming languages using its built-in REST web API interface, and a proprietary Bolt protocol with official drivers; most popular graph database in use as of January 2019.
Neo4J can be used jointly with MongoDB to associate document to the nodes or edges. Please check more details in Neo4j and MongoDB

OrientDB
Recommended if you want both good of a graph database and document database (like MongoDB)
Second generation distributed graph database with the flexibility of documents in one product (i.e., it is both a graph database and a document NoSQL database at the same time); licensed under open source Apache 2 license; and has full ACID support; it has a multi-master replication and sharding; supports schema-less, -full, and -mixed modes; has a security profiling system based on user and roles; supports a query language similar to SQL. It has HTTP REST + JSON API.
OrientDB is acquired by SAP.
ArangoDB
NoSQL native multi-model database system developed by triAGENS GmbH. The database system supports three important data models (key/value, documents, graphs) with one database core and a unified query language AQL (ArangoDB Query Language)
JanusGraph
Like a graph query engine over a database backbone
Open source, scalable, distributed across a multi-machine cluster graph database under The Linux Foundation; supports various storage backends (Apache Cassandra, Apache HBase, Google Cloud Bigtable, Oracle BerkeleyDB); supports global graph data analytics, reporting, and ETL through integration with big data platforms (Apache Spark, Apache Giraph, Apache Hadoop); supports geo, numeric range, and full-text search via external index storages (ElasticSearch, Apache Solr, Apache Lucene).
Amazon Neptune
If you want a managed graph database on AWS

Amazon Neptune is a fully managed graph database by Amazon.com. It is used as a web service and is part of Amazon Web Services. Supports popular graph models property graph and W3C’s RDF, and their respective query languages Apache TinkerPop Gremlin and SPARQL.
Microsoft SQL Server 2017
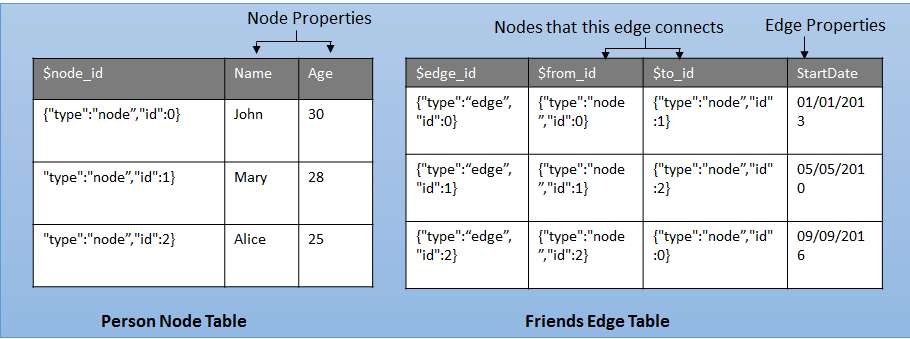
Offers graph database abilities to model many-to-many relationships. The graph relationships are integrated into Transact-SQL and use SQL Server as the foundational database management system.
DataStax Enterprise Graph

DSE Graph is an add-on to DSE that enables enterprises to identify and analyze hidden relationships between connected data to build powerful applications for fraud detection, customer 360, social networks, and real-time recommendations.
Optimized for storing billions of items and their relationships, DSE Graph incorporates all the enterprise-class capabilities of DSE, including continuous availability; linear scalability; advanced security; analytics and full text search; visual management and monitoring; and development tools.


