MEGAVERSE Benchmarking Large Language Models Across Languages, Modalities, Models and Tasks
[llm multimodal deep-learning dataset metaverse benchmark multi-lingual marvl in22 XRiSAWOZ Belebele xm-3600 gpt palm llama This is my reading note for MEGAVERSE: Benchmarking Large Language Models Across Languages, Modalities, Models and Tasks. This paper proposes a new multilingual benchmark to test LLM and provides very limited dataset for multimodality. The language distribution is also strange which houses to much on south, Asia. Overall GPT and Palm get the best performance.
Introduction
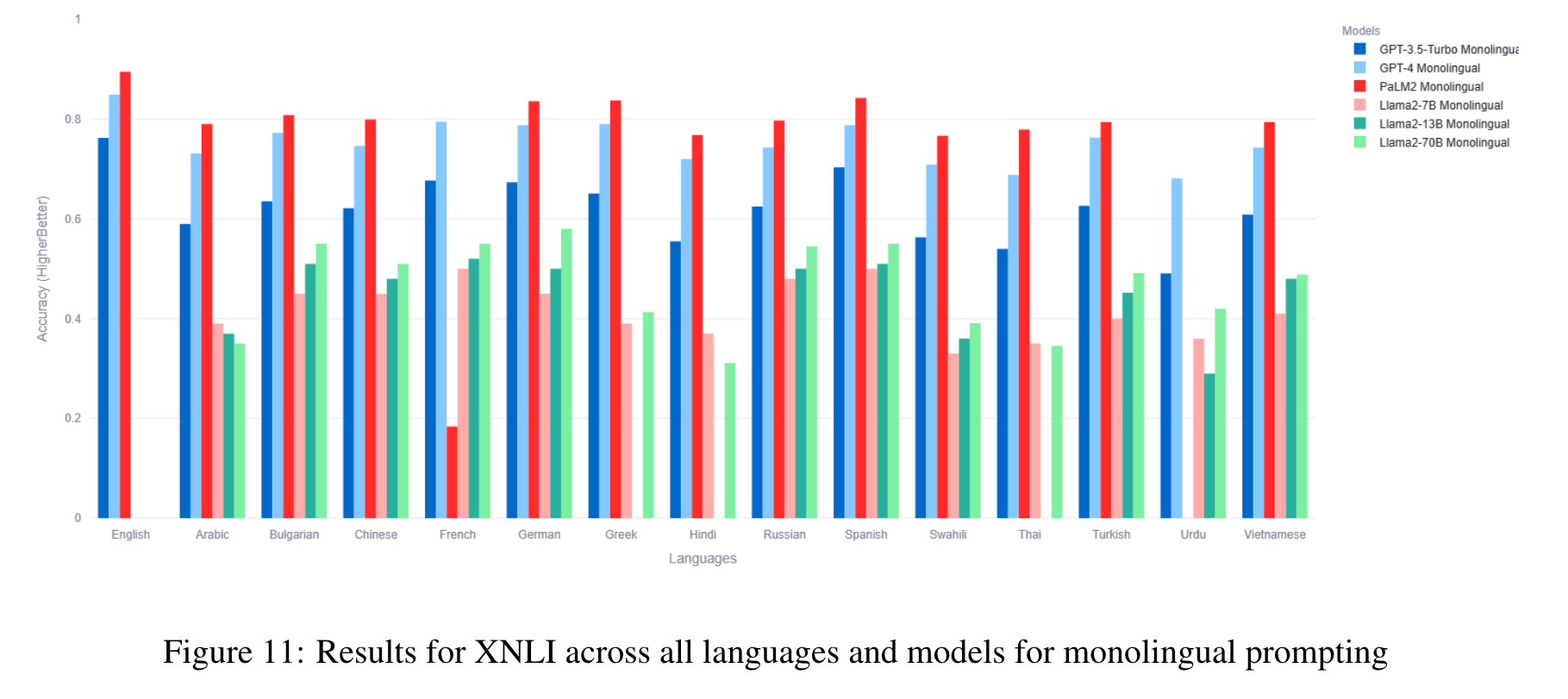
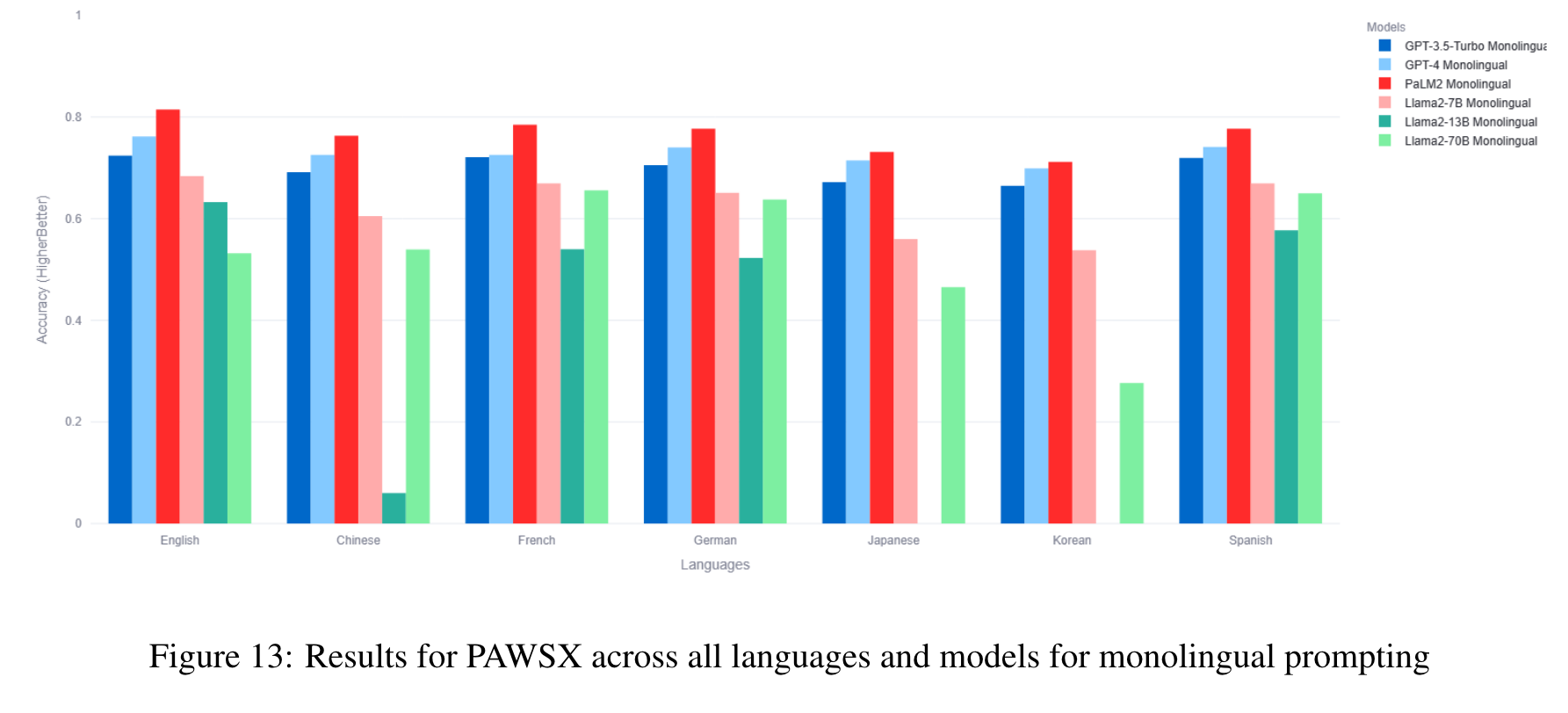
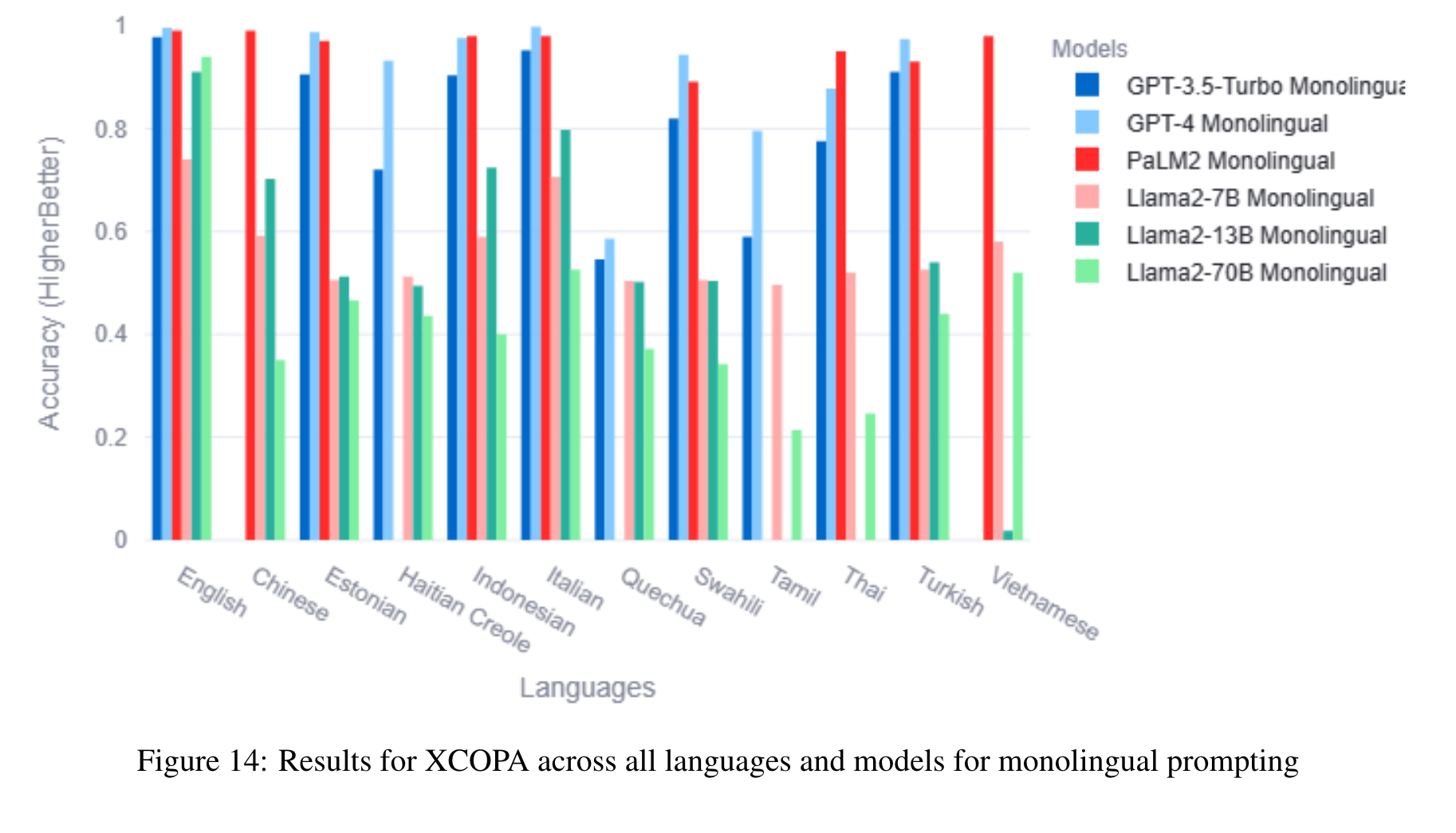
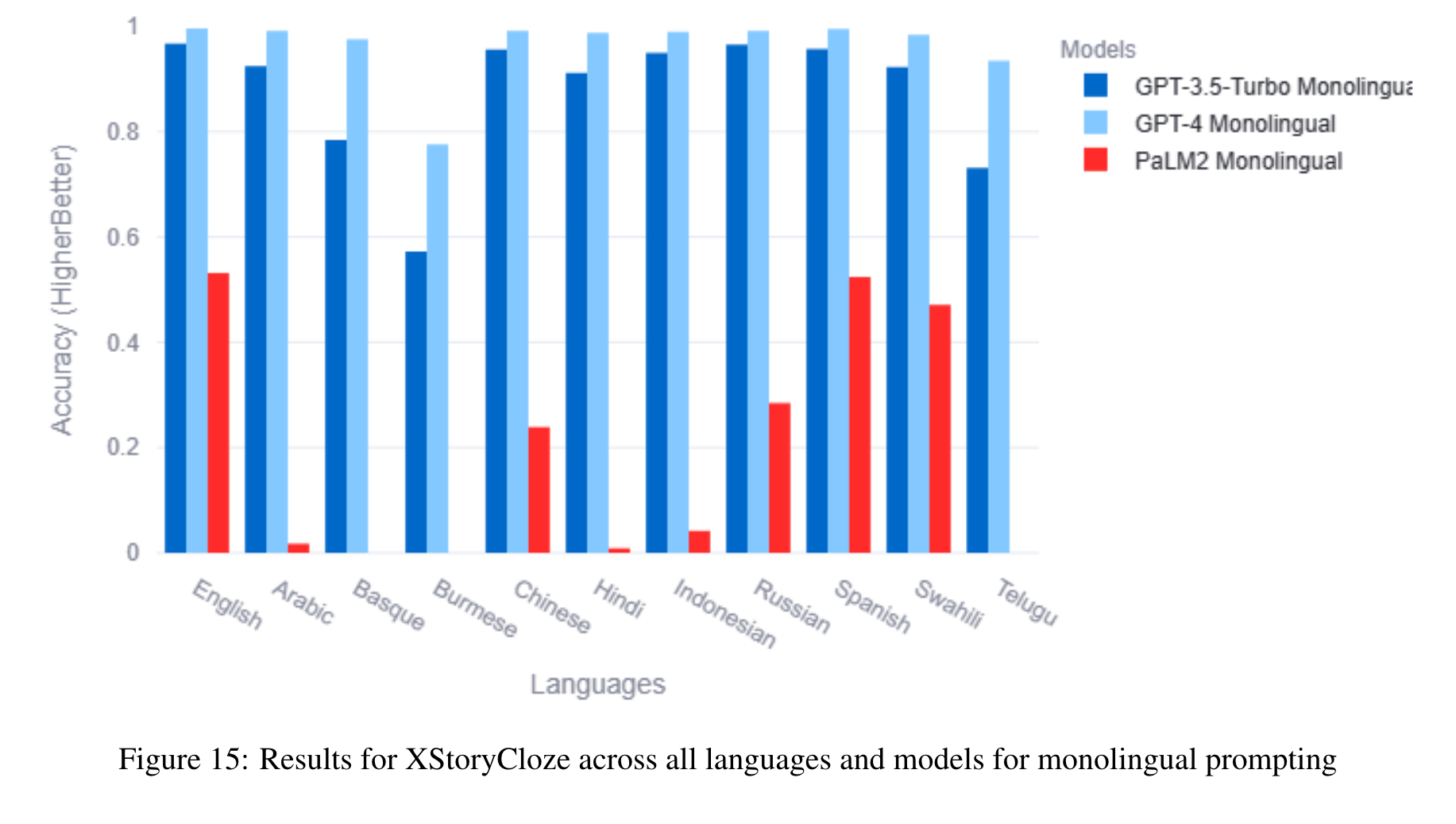
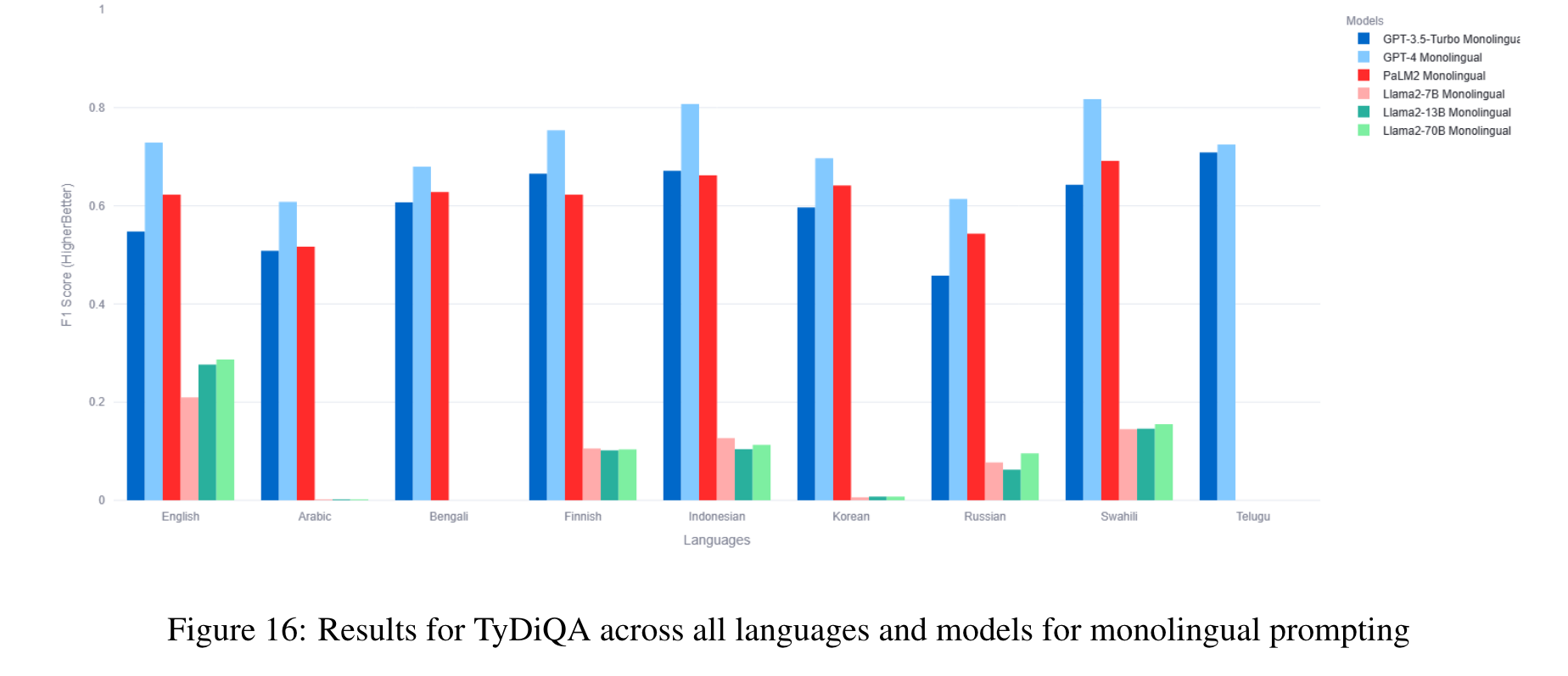
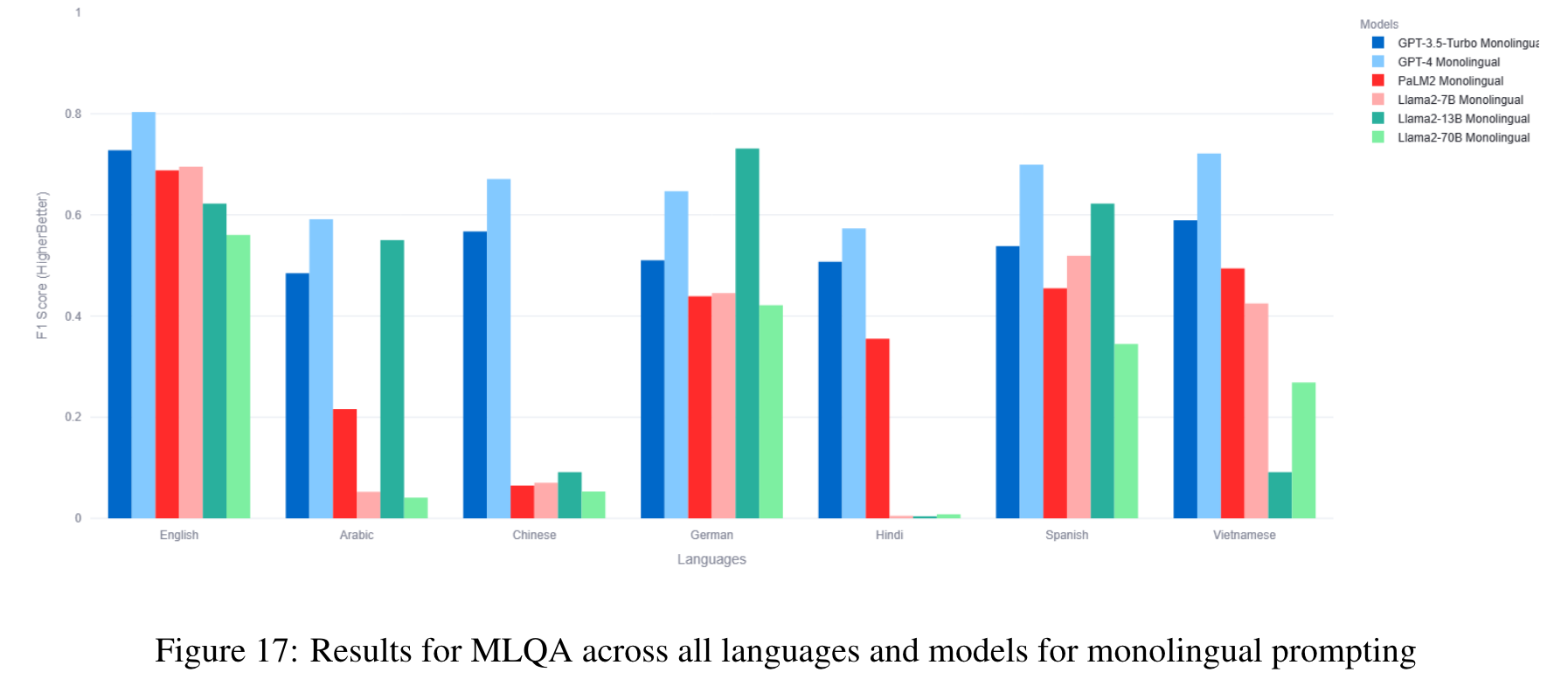
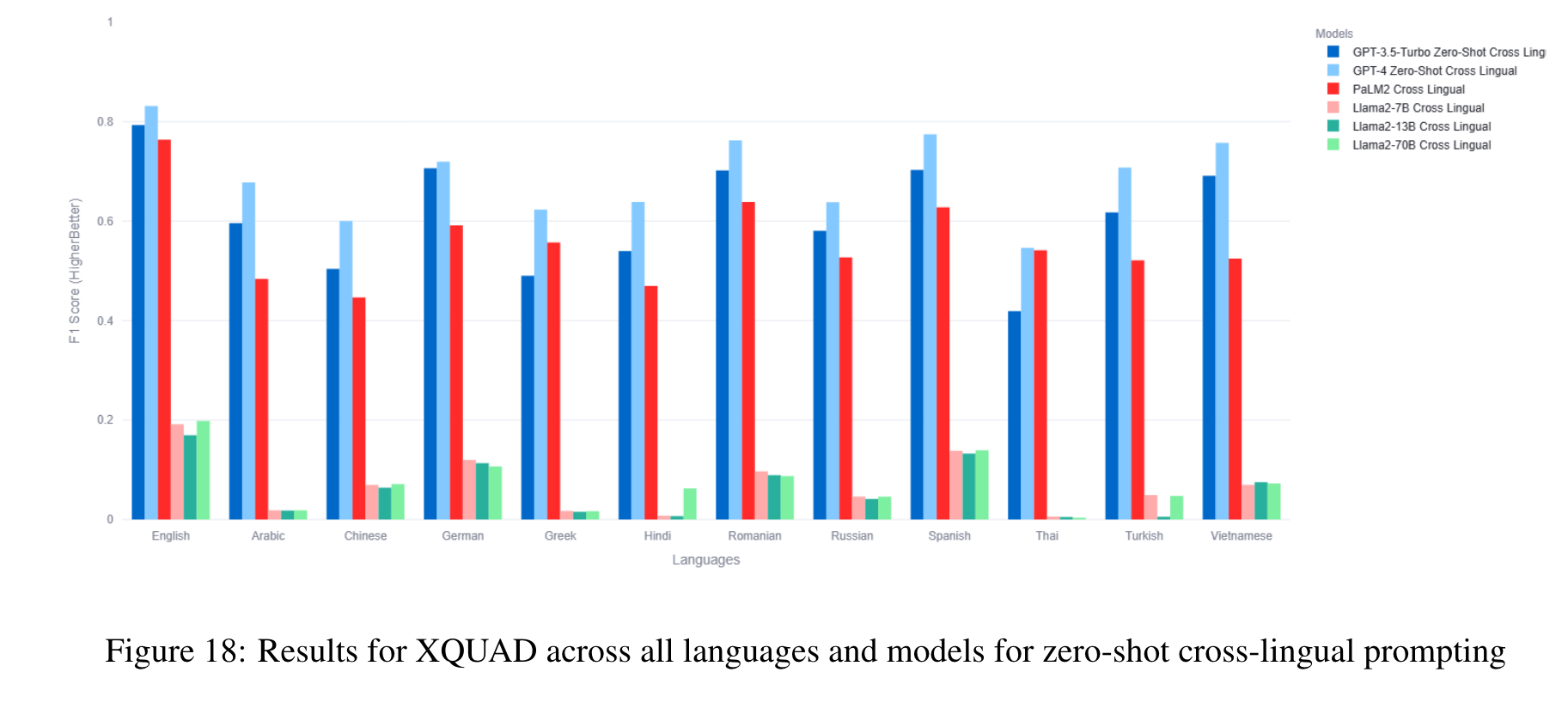
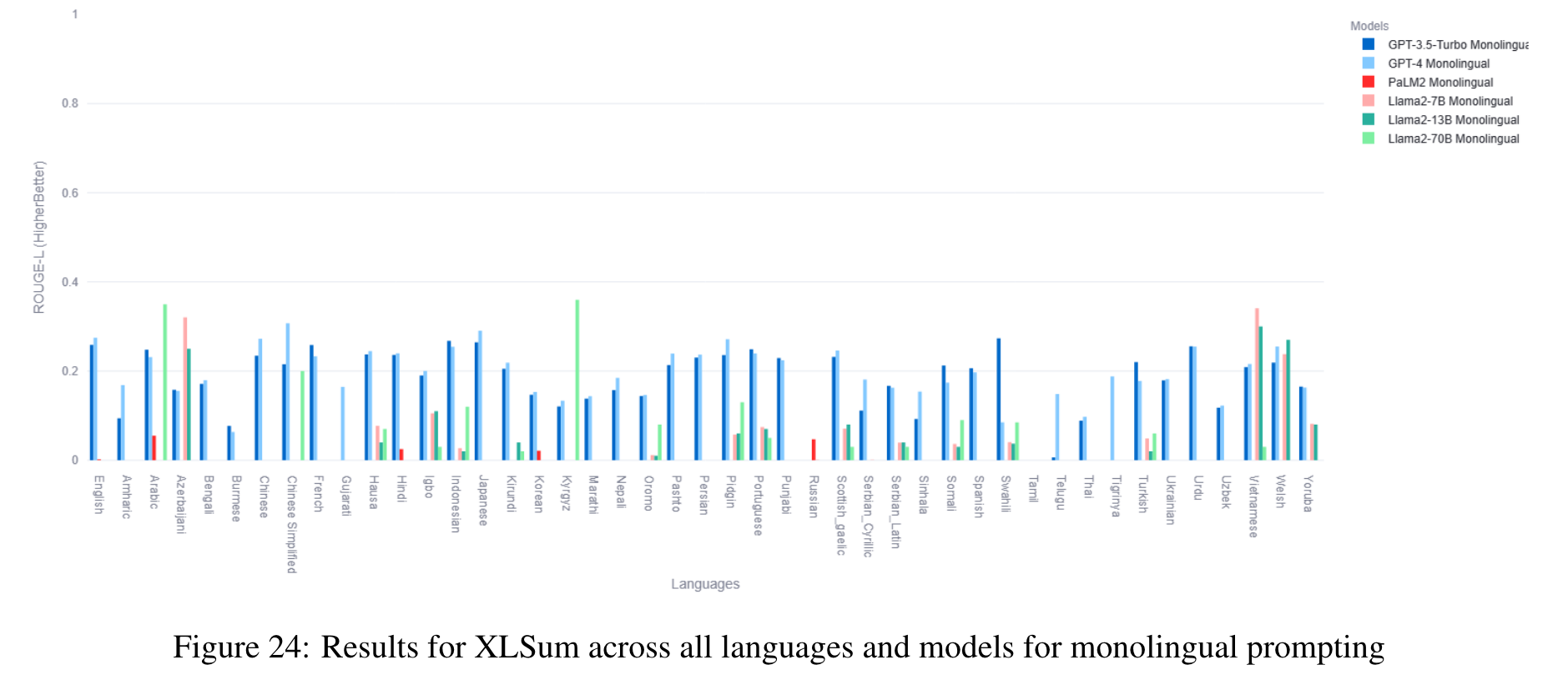
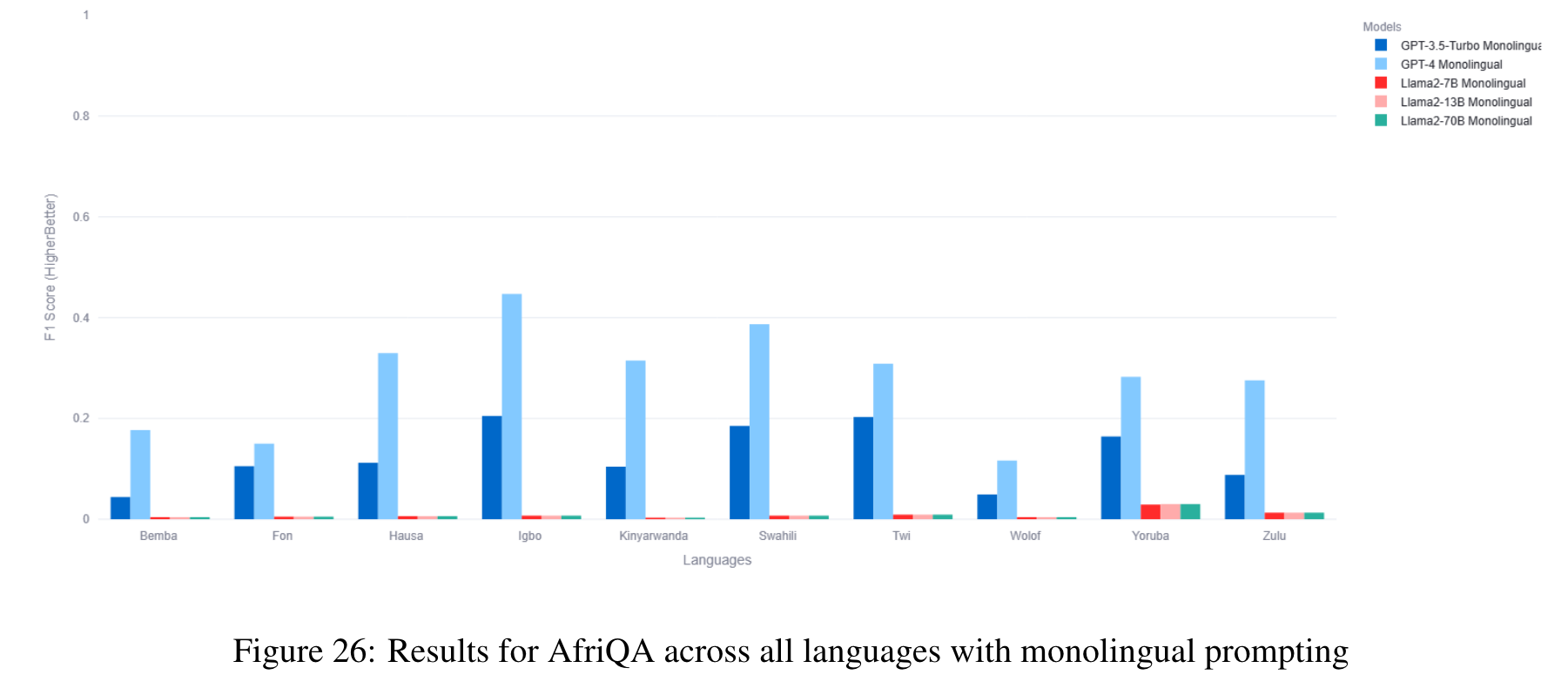
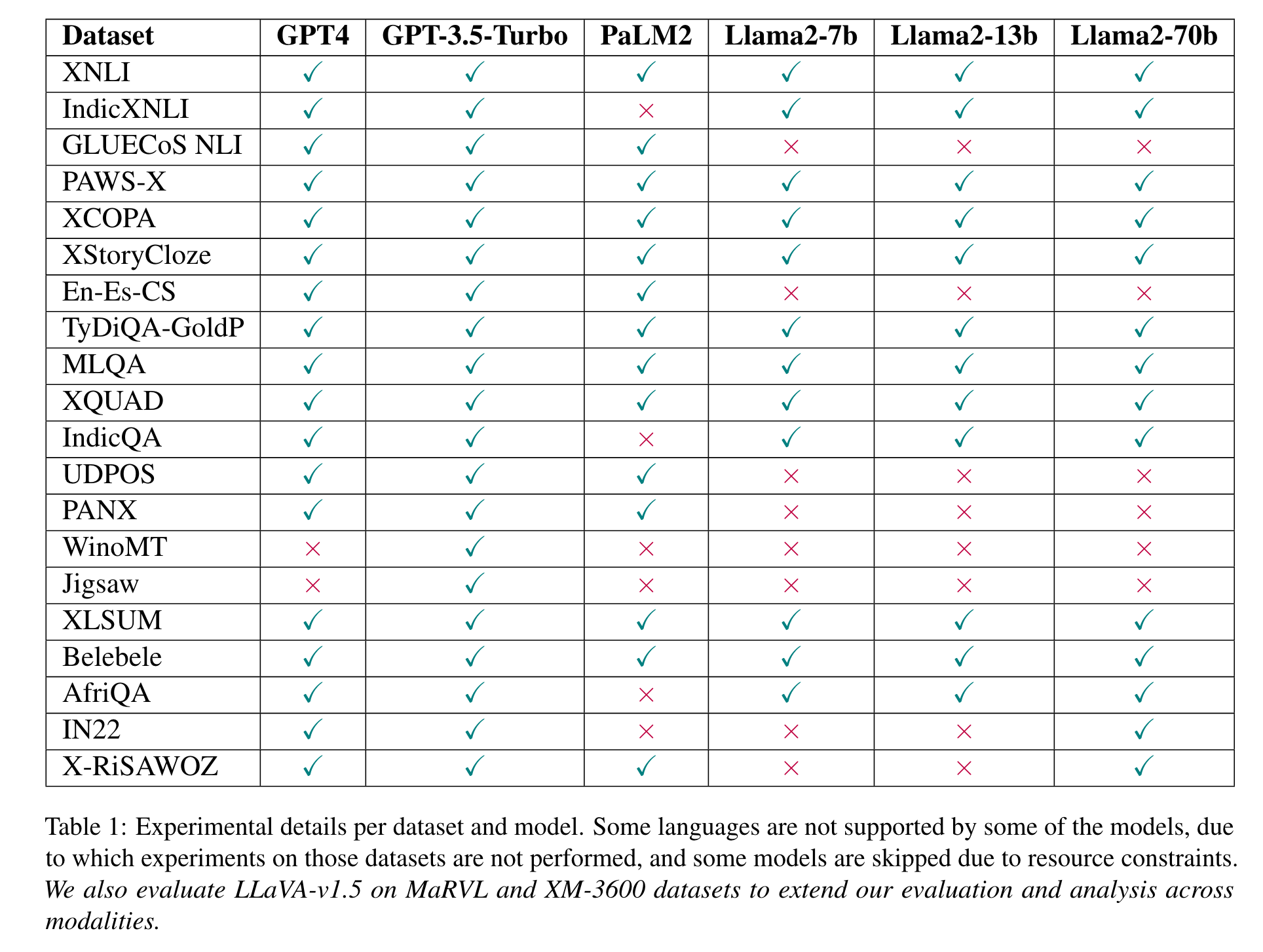
The benchmark comprises 22 datasets covering 81 languages, including low-resource African languages. We evaluate several state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT3.5-Turbo, GPT4, PaLM2, and Llama2 on the MEGAVERSE datasets. Additionally, we include two multimodal datasets in the benchmark and assess the performance of the LLaVav1.5 model. Our experiments suggest that GPT4 and PaLM2 outperform the Llama models on various tasks, notably on low-resource languages, with GPT4 outperforming PaLM2 on more datasets than vice versa. (p. 1)
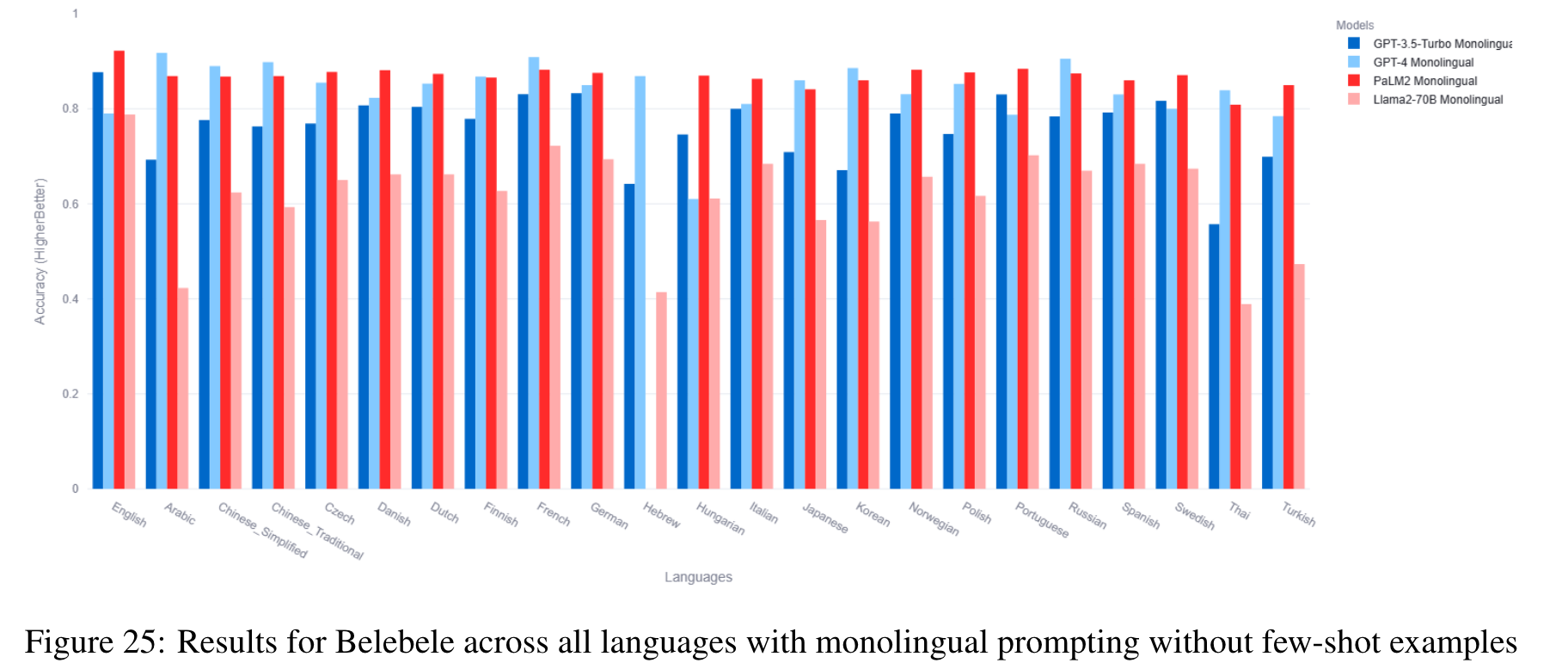
Belebele
Belebele (Bandarkar et al., 2023) is a multiple choice machine reading comprehension (MRC) dataset is parallel across 122 languages. Each question is linked to a short passage from the FLORES200 dataset (Team et al., 2022). The questions were created by human annotators and the human annotation procedure was carefully curated to create questions that discriminate between different levels of language comprehension. This process was reinforced by extensive quality checks. (p. 3)

We perform zero-shot monolingual prompting for our experiments, as this dataset does not have a dev set. (p. 3)
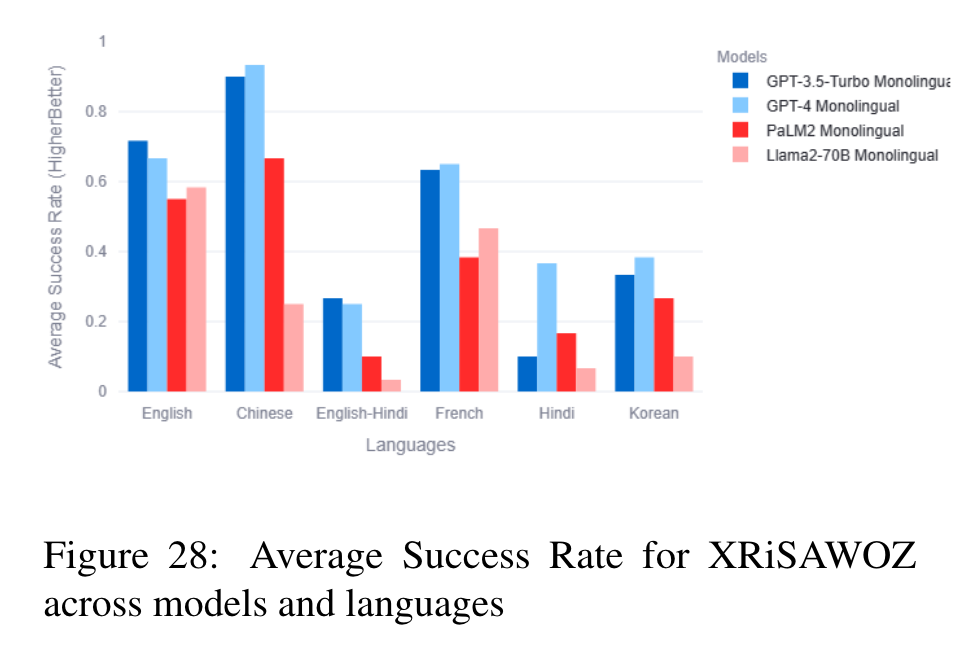
XRiSAWOZ
XRiSAWOZ (Moradshahi et al., 2023) is a (domain specific) task oriented dialogue modeling dataset. The dataset is a multilingual (English, Hindi, French, Korean) translation of RiSAWOZ dataset (Quan et al., 2020) which was Chinese. XRiSAWOZ also includes an English-Hindi code mixed setting. Each dialogue in XRiSAWOZ is confined to a narrow domain and the conversation agent must make use of structured knowledge available in the database to answer user queries. (p. 4)
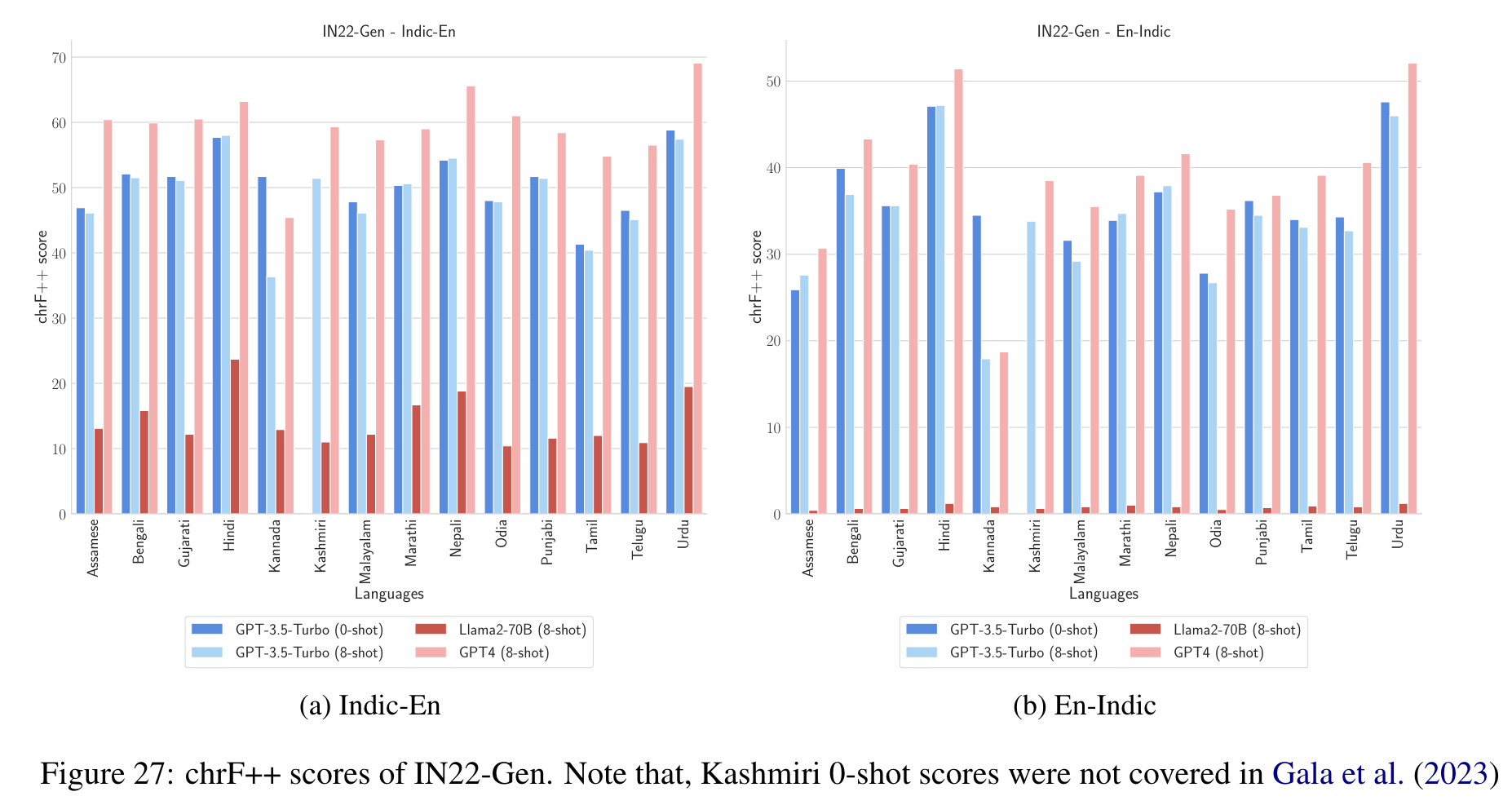
IN22
IN22 (Gala et al., 2023) is a translation benchmark for all 22 scheduled Indic languages which is offered in two flavors, IN22-Gen and IN22-Conv (p. 4)
MaRVL
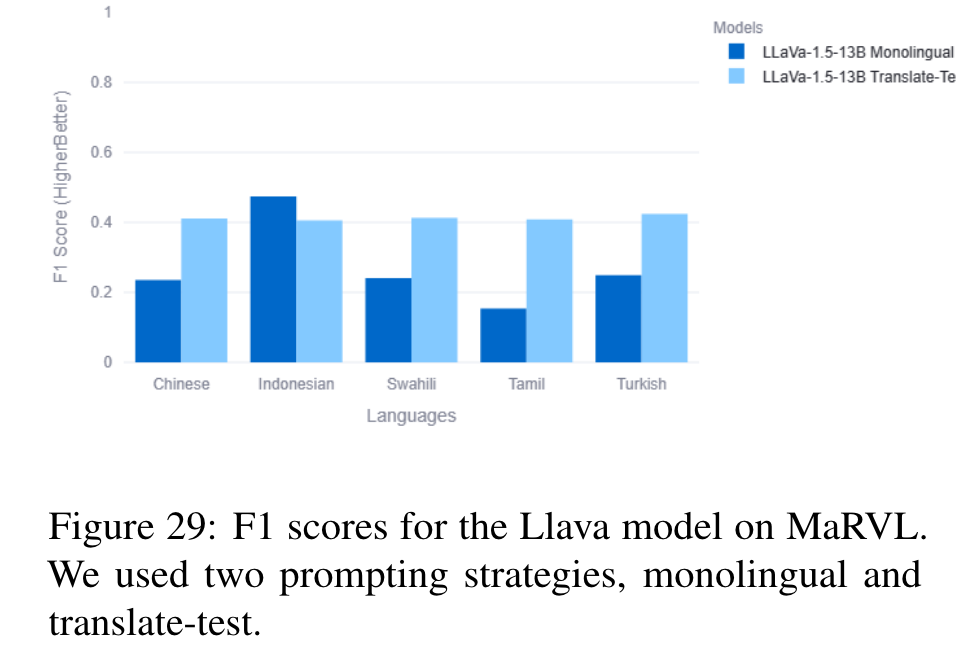
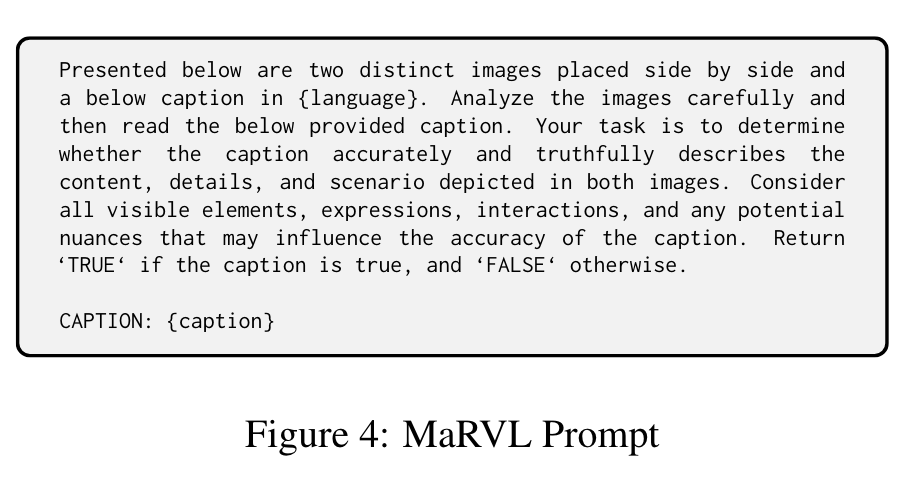
The concepts and images collected were entirely driven by native speakers and are representative of various cultures across the globe and span 5 languages, i.e., Indonesian, Chinese, Swahili, Tamil, Turkish. Each instance in the dataset consists of a pair of images (left image and right image) and a statement, and the task is to determine whether the statement is consistent with respect to the given pair of images. (p. 4)
XM-3600
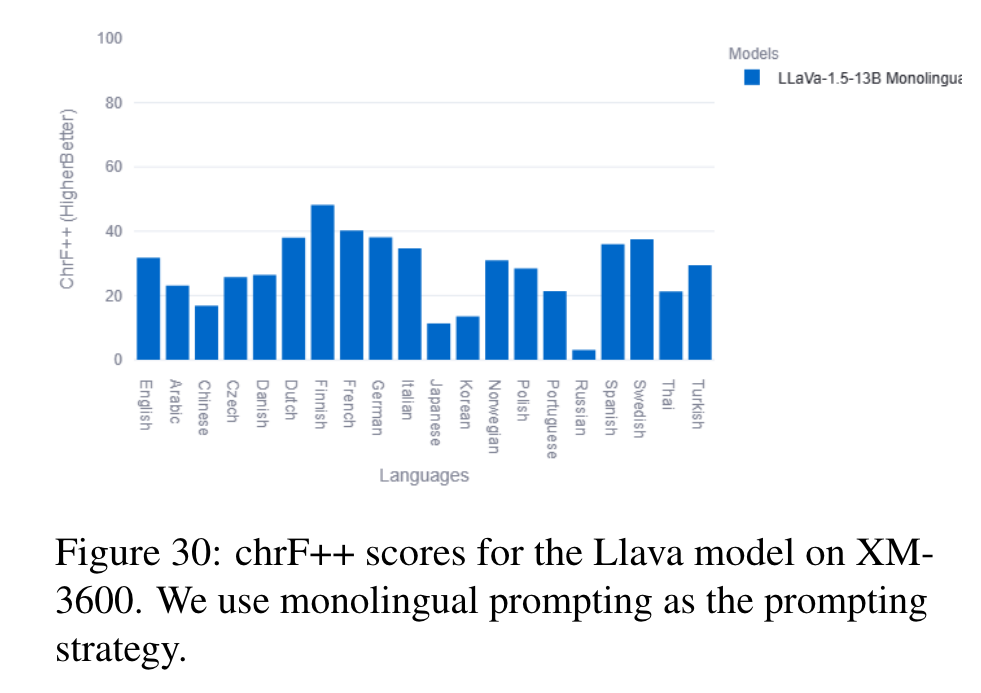
Crossmodal-3600 (Thapliyal et al., 2022) is a multilingual image captioning dataset consisting of 3600 geographically diverse images directly captioned in 36 different languages, avoiding any inconsistencies due to translations. (p. 5)

Prompting strategies
We define five main components to define the prompts:
- a test example x_test for which the predictions are to be made;
- k few-shot exemplars ${(x_i, y_i)}^k _{i=1}$, that are used to provide in-context supervision to the model;
- a task instruction I which describes the instruction in text for the task to LLM
- a prompt template f_temp(x) which turns a dataset input example into a text format that can be used for prompting;
- and an answer verbalizer f_verb(y) that maps the label y to a textual representation. (p. 6)
In our previous work, we show that the monolingual prompting variation outperforms the zero-shot cross-lingual prompting variation for most datasets, with the translate-test variation performing better than monolingual for a few low-resource languages. We find that the gap between translate-test and monolingual prompting is minimal for models such as GPT4, and so for this work default to monolingual prompting except when specified otherwise. (p. 6)
Result