Idea2Img Iterative Self-Refinement with GPT-4V(ision) for Automatic Image Design and Generation
[llm-agent self-reflective reflextion multimodal llm stable-diffusion diffusion idea2img feedback mm-react conversation deep-learning tool chatgpt text2image self-refine control-net This is my reading note for Idea2Img: Iterative Self-Refinement with GPT-4V(ision) for Automatic Image Design and Generation. This paper proposes a system on how to use GPT4V to generate images from idea by calling an image generation tool. Especially.it generates text prompt based on idea, given the images generated from the prompt, it ranks and selects the best image; it then generate a new promote to guide image generation process.
Introduction
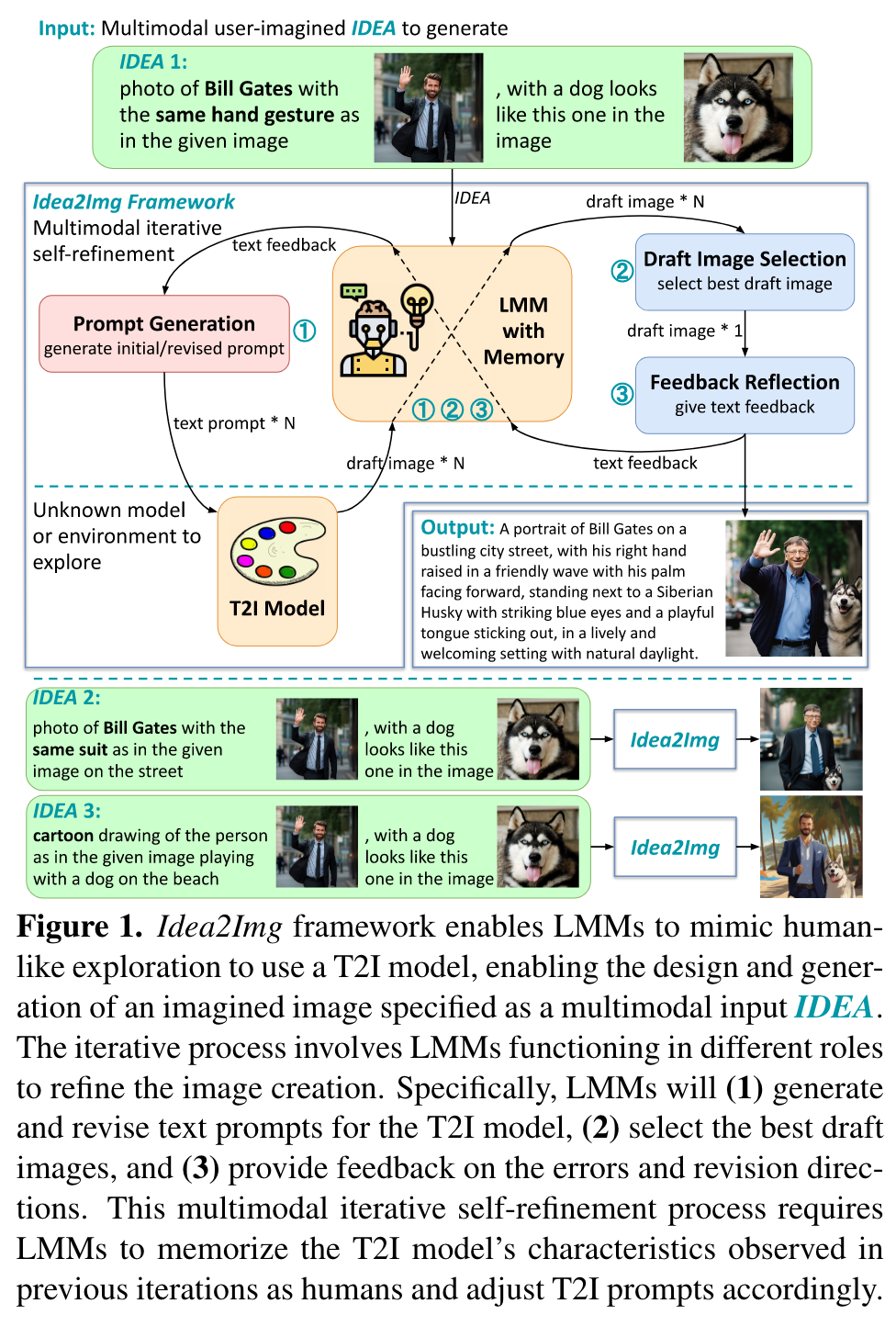
We introduce “Idea to Image,”1 a system that enables multimodal iterative self-refinement with GPT-4V(ision) for automatic image design and generation. Humans can quickly identify the characteristics of different text-to-image (T2I) models via iterative explorations. This enables them to efficiently convert their high-level generation ideas into effective T2I prompts that can produce good images. We investigate if systems based on large multimodal models (LMMs) can develop analogous multimodal self-refinement abilities that enable exploring unknown models or environments via self-refining tries. Idea2Img cyclically generates revised T2I prompts to synthesize draft images, and provides directional feedback for prompt revision, both conditioned on its memory of the probed T2I model’s characteristics. The iterative self-refinement brings Idea2Img various advantages over vanilla T2I models. Notably, Idea2Img can process input ideas with interleaved image-text sequences, follow ideas with design instructions, and generate images of better semantic and visual qualities. (p. 1)
Iterative self-refinement is one intrinsic ability humans possess when exploring unknown environments and solving complicated problems. Large language models (LLMs) agent systems [9, 23, 40] have demonstrated the effectiveness of self-refinement in better addressing natural language processing tasks (p. 3)
The LMM will act in different roles to analyze the return signal from the T2I model (i.e., draft images) and design the next round’s queries (i.e., text T2I prompts). The three roles of generating T2I prompts, selecting draft images, and reflecting feedback together enable the multimodal iterative self-refinement ability. (p. 3)
Furthermore, Idea2Img is enhanced with a memory module that stores all prompt exploration histories, including previous draft images, text prompts, and feedback. (p. 3)
Related Work
Idea2img is inspired by the effectiveness of iterative self-refinement in LMM-based agent systems [23, 29, 40] in exploring unknown environments and tasks, built upon the successful LLM agents [14, 30, 32, 37, 47, 52, 57]. Self-refine [23] takes the same LLM to iteratively critique its outputs, and leverage this feedback to enhance its predictions. Reflexion [40] explores a self-reflective LLM system on the text-based environment exploration task [41] and multi-hop QA [50]. (p. 3)
For instance, MM-ReAct [49] integrates an LLM with multiple vision tools for multimodal reasoning and action, enabling it to solve various complicated visual understanding tasks, ranging from multi-hop document reasoning to open-world video interpretation. Visual ChatGPT [45] empowers ChatGPT to allocate various image generation models, such as Stable Diffusion [34], img2img model [24], ControlNet [56], enabling multi-step visual editing and generation. (p. 4)
Existing studies assume the knowledge of how to use each tool, and provide such information to LLMs via text instructions or incontext examples. (p. 4)
Idea2Img Framework

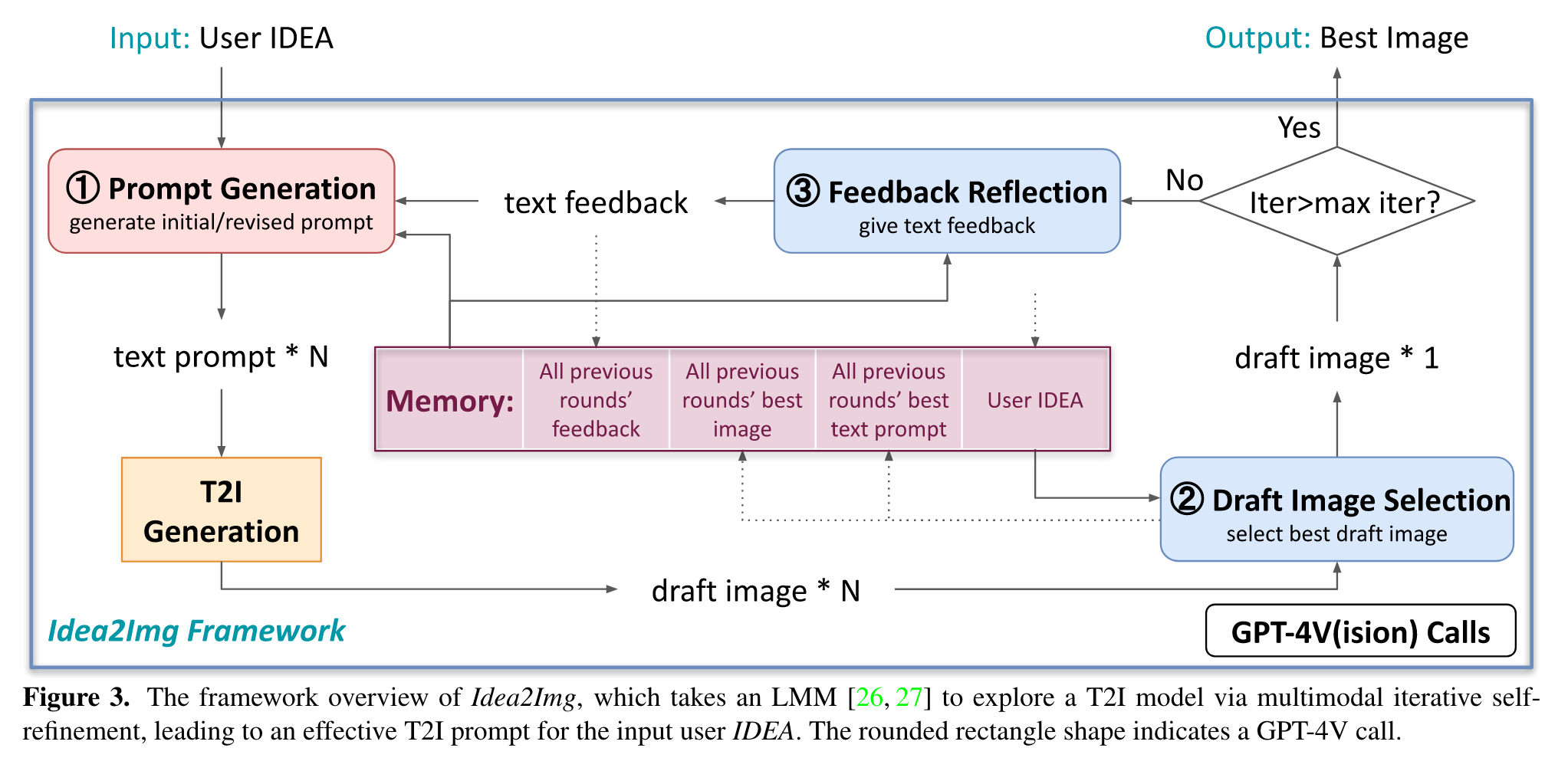
Initial prompt generation
IDEA can take multiple images and use interleaved text instruction to extract arbitrary visual information of interest (p. 4)
Draft image selection
The task of selecting the best image requires M to compare and grade both the semantics and visual quality of N similar draft images. We find such a “spot the difference” task very challenging for LMMs, and only the very recent model [26] is capable of performing the selection reliably. Qualitative examples are shown in Figure 10. (p. 4)
Feedback reflection
“Feedback reflection” aims to provide text feedback ft that describes the direction to improve for draft image i∗t . The steps prompts M with LMM prompt pf b, conditioned on the draft image i∗t and memory m: (p. 5)
The step not only requires M to identify the discrepancy between image i∗t and IDEA x, but also benefits from writing the major errors to make the iteration effective. In practice, we find it helpful to explicitly specify the aspects to check, such as style, entity, attributes, appearance, etc., via text instructions or in-context examples in LMM prompt pf b. Furthermore, we add text instructions to pf b to have M “focus on one thing to improve in each feedback,” and “provide a high-level explanation of how to modify prompts to address the given feedback.” Example feedback is shown in Figure 8. (p. 5)
Revised prompt generation
Finally, “prompt generation” takes text feedback ft and memory m to draft N revised prompt y^0{t+1}, . . . , y^{N−1}{t+1}, by prompting M with LMM prompt previse (p. 5)
Memory module
Memory m is one important design in Idea2Img. m has the format of interleaved image-text sequences that store all previous iterations’ feedback, selected draft image, and the corresponding text prompts (p. 5)
Experiments
Experiment Settings
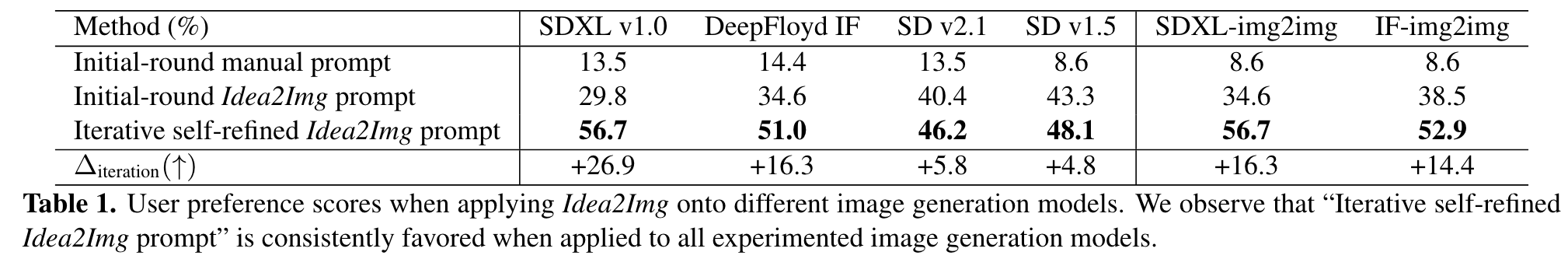
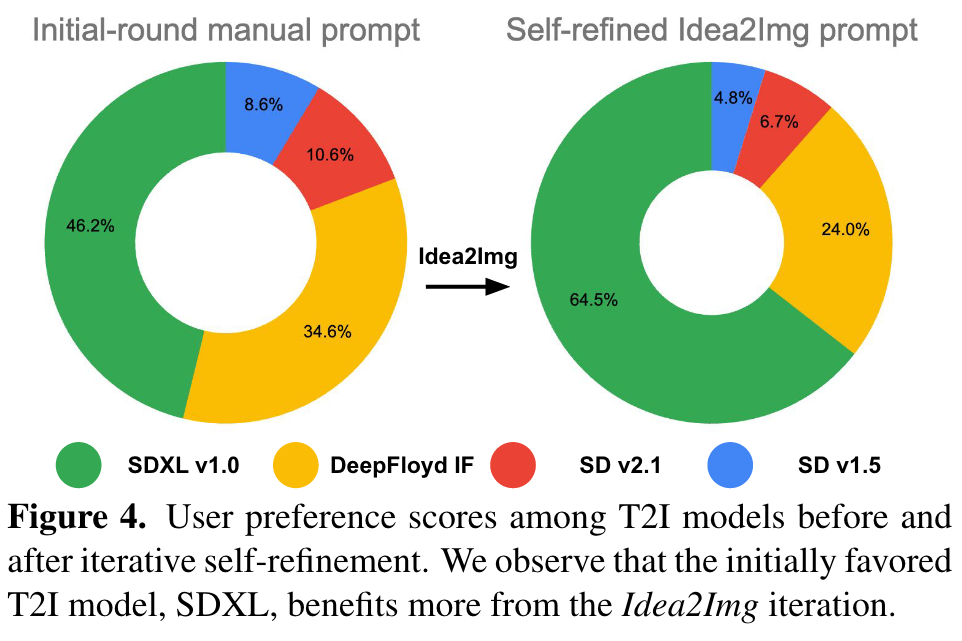
- “Initial-round manual prompt” is the baseline T2I prompt written by humans with minor prompt engineering. It serves as the baseline of a T2I prompt that merely contains key information in IDEA.
- “Initial-round Idea2Img prompt” is the LMMgenerated T2I prompt in the initial round. Specifically, the max iteration T = 1, and LMM M is only used for initial prompt generation and draft image selection, but not feedback reflection nor revised prompt generation. This Idea2Img variant is used to ablate Idea2Img’s gain from prompt generation and selection, vs. the further iterative refinement.
- “Iterative self-refined Idea2Img prompt” is complete Idea2Img pipeline with the max iteration T = 3. (p. 6)

LMM Feedback, Revision, and Selection
Feedback reflection
Figure 8 shows the text feedback generated by GPT-4V for the user IDEA and the draft image and T2I prompt. Idea2Img can effectively check if the generated image is correct, such as the number of oranges in (a) and the misspelled scene text ”ALURE RESEACHE” in (b). In addition to text descriptions in IDEA, Idea2Img can verify if the draft image corresponds to the visual descriptions in IDEA. This includes the color and breed of the dog in (e), the exact art style in (f), and the same cloth and pose in (g). Furthermore, Idea2Img can understand and verify the IDEA containing interleaved image-text pairs, as shown in Figures 8(h,i) (p. 10)
In addition to identifying the discrepancy, Idea2Img also points to the plausible directions that may improve the T2I prompt in the text feedback. (p. 14)

Revised prompt generation
For example, (a) the revised T2I prompt includes a detailed description of the “yoga dolphin pose” to generate the correct body pose; (b) the revised T2I prompt mentions “an empty plate with no other objects” to avoid the T2I model misunderstand the prompt “no bananas;” (c) T2I model generates the correct hand gesture with Idea2Img providing text description on how to take a screenshot. (p. 14)

Draft image selection
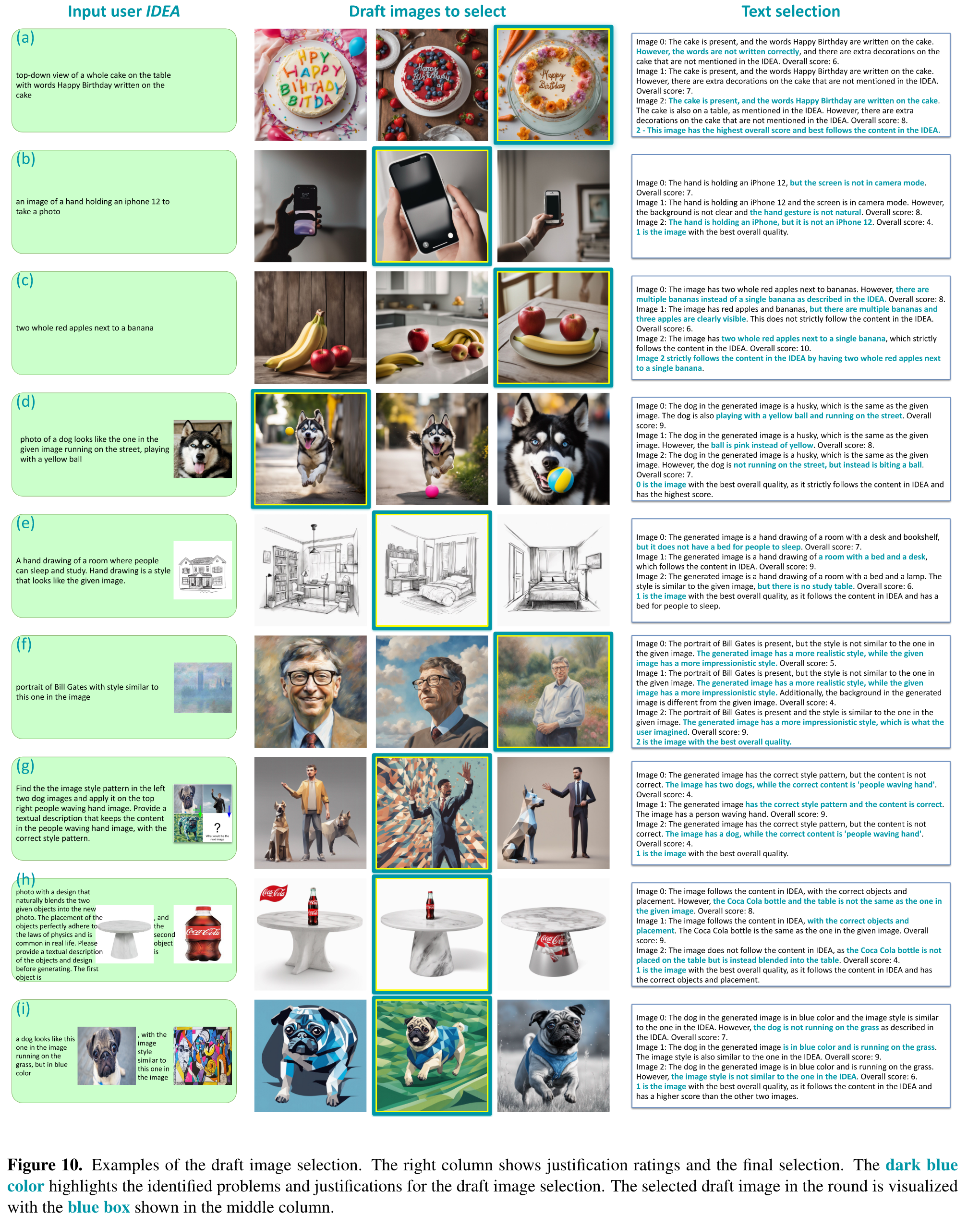
The LMM prompt is designed such that GPT-4V gives justifications and scores for each draft image, in addition to the final selection index. Such intermediate thoughts not only help humans interpret the selection process, but also serve as the chain of thought to improve the selection performance. We observe that GPT-4V can compare different aspects mentioned in the IDEA and give reasonable scores and selection index. (p. 14)
